Key Takeaways:
- Accounts payable is the amount which the company will pay to its suppliers from whom the company has purchased any goods or services on credit.
- It is shown in the balance sheet under the heading ‘Current Liabilities’.
- A higher or increasing payables shows that the company is having higher credit days from the supplier maintaining a healthy growing relationship with the supplier.
- A continuous rise in it will decrease the chance for the company to borrow the cash to meet the short term capital requirement.
- On the contrary, if the company faces liquidity issue then the rise in Accounts Payable spells doom for the company.
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| What Is Accounts Payable? |
| Accounts Payable Example |
| Where Do I Find Accounts Payable? |
| Why it Is Important? |
| What Are Accounts Payable Days? |
What Is Accounts Payable?
Company when purchases goods, it is not always in monetary terms, purchases are also made in credit.
What this means is, the company receives goods and services immediately from the seller and then receives an invoice from the seller which asks to pay money later to them.
This is the liability for the company and comes under the head ‘CURRENT LIABILITY’ as Accounts Payable.
It is a liability, due to a particular supplier when the purchase of goods and services happens without paying cash immediately.

Accounts Payable Example:
Suppose you have a company named ABL ltd and it’s a tool company.
The company purchases 40 hammers for Rs. 40,000 and no money is paid. Instead, the seller gives an invoice to the company stating 90 days of the creditor’s days, stating that within this time period company needs to pay the amount to the buyer.
So, the company will record an account payable when it receives the hammer from the buyer. From the date of purchase, till the date money is paid to the supplier, the company will have an account payable of Rs.40,000.
Gain comprehensive knowledge of company assets with Company Valuation Course by Market Experts
Once the payment is made to the supplier, the cash in hand in the balance sheet reduces and payables will also decrease by the same amount.
(Note: when a purchase is made by the company then purchases increase by Rs. 40,000 and in order to balance the balance sheet the same is recorded as an account payable.)
Where Do I Find Accounts Payable?
They are classified as a liability because it is a debt for the company which it has to pay sooner or later within a year.
You can find it under the ‘Current liability’ section in the Balance sheet.
This is shown in the image:
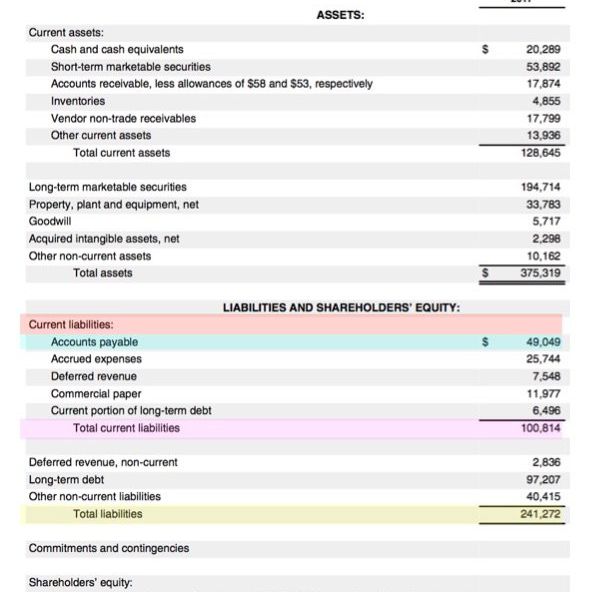
Why it Is Important?
As a company needs to manage the cash inflow as it reflects the company’s future cash flow, in the same way, the company needs to manage its outflow of cash.
Maintaining it helps the company to make a good relationship with suppliers so that they can get good discounts, good negotiable terms with suppliers.
Suggested Read – Accounts Receivable – Formula, Importance & Impact
This strong relationship with suppliers helps to increase the account payable days for the company at a time when the company needs cash urgently to invest in any good opportunity.
What Are Accounts Payable Days?
It shows the average number of days of credit that the company has from its suppliers. A high ratio indicates that the company is taking a long time to pay its suppliers. This can be because the company has obtained a long credit period from its suppliers and thus it will benefit the Company’s cash flow.
Formula:
This is calculated by dividing the average Accounts Payable by the total purchases for the period and multiplying it by 365 days. Most often this ratio is calculated at year-end when Annual reports are available.
Accounts Payable Days: ( Average accounts payable/Cost of Goods Sold)*365
Average Accounts Payable: (Previous year + Current year)/2
Let us understand this with an example:
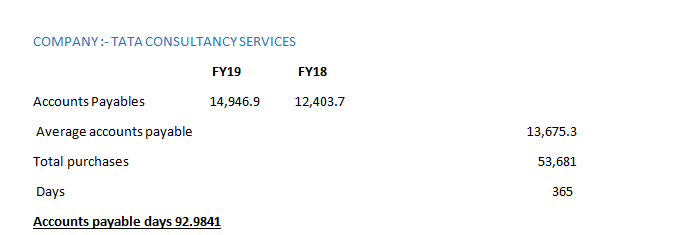
As on Dec FY19, current liabilities is Rs.70,582, under which accounts payables is Rs.14,946.9. This shows that the company has lower days as of around 93 days. This means that the company pays cash to its creditors on time.
Impact:
For continuous business operation paying money to the creditors on time will help the company to make healthy relation with suppliers as this will benefit the company in future for higher discounts and other privileges.
But keeping these days lower is also not good as the company will not have enough cash to invest in the future if it finds good opportunities.
Keeping the accounts payable ratio higher will be beneficial for the company in terms of cash creation.
Let us understand this with an example:

The company takes approximately 206 days to give cash to its suppliers. It means the company is getting higher payable days from its suppliers.
This high Account Payable days gives the company the benefit to maintain its cash flows.
Thus it is the amount company which company needs to pay to the suppliers from whom the company has purchased on credit.
Higher/increasing Accounts Payable shows the company has got larger creditors days from its suppliers thus keeping the cash to invest in different activities.
A continuous rise in Accounts Payable for a strong company will not put the company in a position to borrow cash for short-term capital needs.
In the case of a weak company if it is on a rise then that means that the company might be facing some liquidity issue.
In order to get the latest updates on Financial Markets to visit stockedge
Happy Learning!








