When starting to trade options, it is very important to understand how they work. You must have encountered the options trading terms call and put options.
But you must be wondering how to trade these options and what the key features of options trading in India are. So, let’s first understand what call options are, and then let’s explore call options further with an example.
Table of Contents
What is a Call Option?
A call option is an options contract in which the buyer has the right to buy a specified quantity of the underlying stock at a predetermined price without any obligation.
Now let us understand this with an example:
Let us assume that a stock is trading at Rs.100 today.
Today, you are getting a right to buy the same stock one month later, at, say, Rs. 100 but only if the share is trading at the price of more than Rs. 100.
Should you buy it?
The answer is yes, as this means that even after one month, if the share is trading at Rs. 120, you can still buy it at Rs.120. To get this right, you need to pay a small amount today, say Rs.5.
Now, if the share price goes above Rs. 100, you can exercise your right to buy the shares at Rs. 100. If the share price stays at or below Rs. 100, you do not need to buy the shares.
You just lose Rs. 5, which you had paid for the right to buy in this case. This type of options contract is known as the Call Option.
What are Long Call Options?
When traders expect the price to move up, they can take a long position in the call option. Investors pay a premium to buy a long call option, and they do so in the expectation of improved profits.
However, if the price drops below the strike price, the option holders lose the premium paid. For example, let us assume that the stock’s strike price is Rs. 5000 and the premium is Rs. 35.
It is anticipated that its price will increase in the following month. As the holder of a call option, you can retain your right to purchase a specified quantity of shares.
The premium is the maximum amount that a buyer will agree to suffer as a loss. If the price of the share increases in the following month, the buyer can exercise this call option.
If the share’s price does not increase beyond the strike price of Rs. 5000, the option expires after that date. Thus, the buyer incurs a loss of Rs. 35 on the premium.
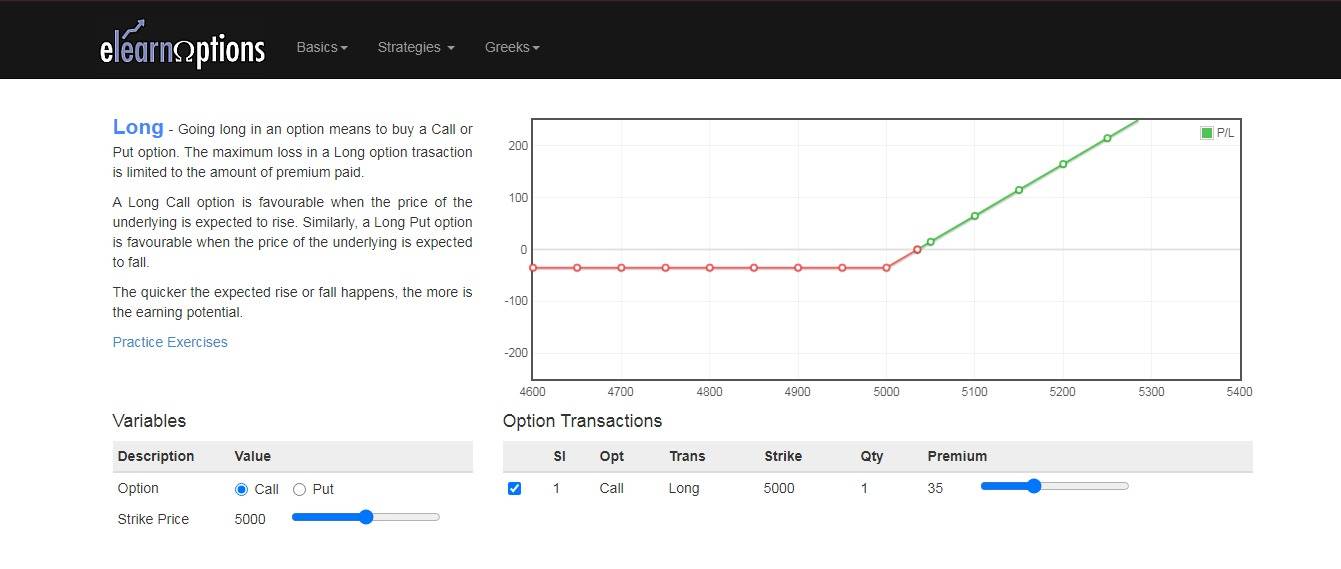
From the above diagram, you can see that your profits will be unlimited if the price moves up, and losses will be limited to the premium.
What is Short Call Option?
The short-call options involve selling an option of a given underlying asset at a predetermined price.
This strategy leads to limited profit if shares are traded below the strike price, and it attracts substantial risk if it is sold at a value more than its strike price.
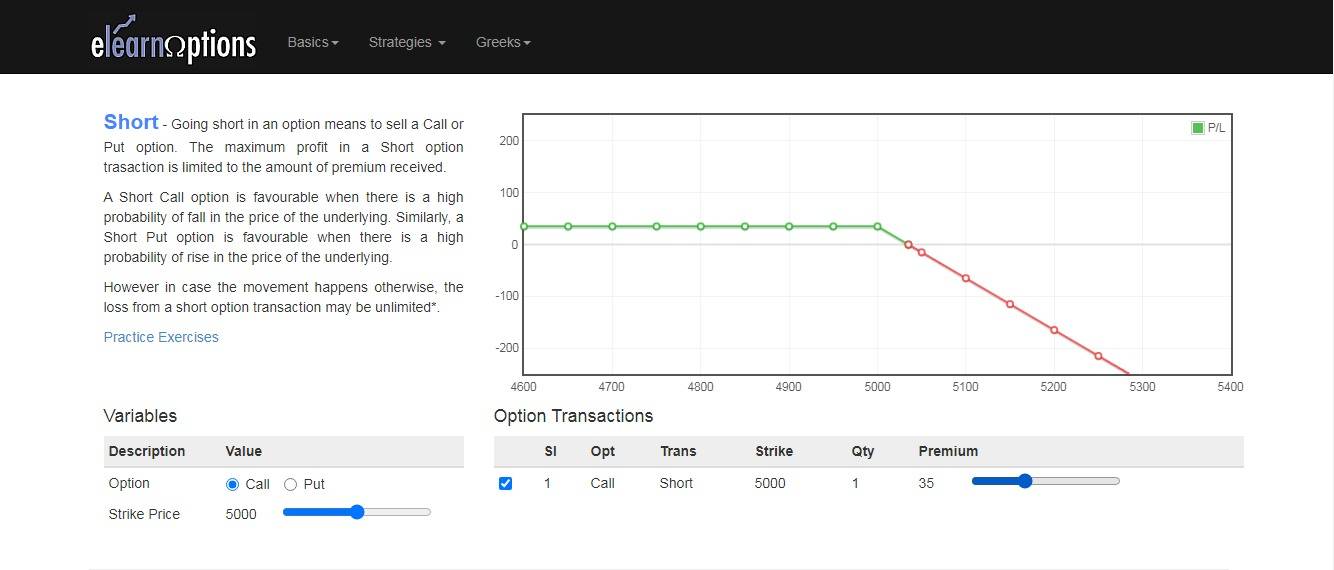
From the above diagram, you can see that when shorting a call option, the profit is limited to its premium amount, which is Rs. 35, and the loss is unlimited.
What are Index and Stock call options?
An index call option is the right to buy an index, and the profit or loss depends on the movement in the index’s value.
For example, Nifty Calls, Bank Nifty calls, etc.
The stock options are options on individual stocks, such as options on Reliance Industries, Tata Steel, Infosys, and Adani SEZ.
The principle of trading call options is the same in both cases. When we buy call options, then we expect the price of the stock or index to go up.
What are Monthly and Weekly call options?
Monthly call options expire on the last Thursday of every month. SEBI has introduced a new product called weekly options, specifically for Bank Nifty. The main idea is to reduce the risk of options by making the expiry each week.
What are ITM and OTM call options?
In-the-money (ITM) call options are those in which the market price is more than the strike price.
Similarly, the out-of-the-money (OTM) call option is one in which the market price is lower than the strike price.
For example, if the market price of ITC Ltd. is Rs.180, then the 170 Call Options will be ITM, while the 200 Call Options will be OTM.
Difference between Call Options and Put Options
An investor buys a put option when he expects the price of an underlying asset to fall within a specific time.
Below are the differences between the Call Option and Put Option:

What influences the price of the call option?
Many factors influence the price of the call option, with the strike price and the market price being important.
Political events that cause uncertainty and volatility in the market may push up the price of these options.
In case you are willing to learn about options trading, click here: Option Trading Made Easy
You can also use the StockEdge web version to use option scans to filter out stocks for trading the next day.
Bottomline
A call option is an option contract in which the buyer has the right to buy a specified quantity of the underlying stock at a predetermined price without any obligation. When traders expect the price to move up, they can take a long position in the call option. A short call option involves selling an option on a given underlying asset at a predetermined price. An index call option is the right to buy an index and the profit or loss depends on the movement in the value of the index. Many factors influence the price of the call option, the strike price and the market price being important factors.