Retention ratio is also known as Ploughback ratio.
It is a fundamental analysis ratio that measures the proportion of earnings that is retained back in the business rather than being paid out as dividends to shareholders.
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| Formula to calculate Retention Ratio |
| How Retention Ratio is useful to analyze a stock? |
| What are the factors that affect the retention ratio? |
| What are the limitations? |
It is the opposite metric of Dividend Payout Ratio.
At the end of every fiscal a company generates earnings that may be positive (profits) or negative (losses).
A company with profits provides its management with ample space to utilize this surplus for a number of purposes.
They may decide to pay the entire profit to the shareholders as dividends, can retain it to reinvest for growth purpose or can also opt for a combination of both.
When a company chooses to retain profit or a portion of profit for future growth purposes it is called Retained Earnings, which when expressed as a percentage of total earnings is Retention Ratio.
The retained profit is transferred to the reserve & surplus in the balance sheet which increases the equity of the company proportionately.
Formula to calculate Retention Ratio
The retention Ratio can be calculated using the following two formulae:
(i) The first method to calculate retention ratio involves dividing the increase in retained earnings during the period by net income of the period. That is,
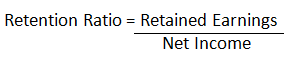
Where, Retained Earnings = Net Income – Dividend Distributed for the year.
(ii) Another possible way to calculate the ratio is by determining the residual funds on calculating the payout ratio. That is,
Retention Ratio =1- Payout Ratio
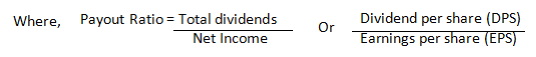
Thus, from the above we understand that the ratio indicates the amount of net profit that has been retained back into the company so that it can be reinvested for future growth and expansion of the business.
How Retention Ratio/Plowback Ratio is useful to analyze a stock?

What are the factors that affect the retention ratio?
When a company is growing, it needs additional cash to finance investment in tangible and intangible assets and also in marketing activities to capture a larger customer base.
When a company is looking to explore an acquisition or takeover opportunities that align with its growth and expansion objectives, it will have a higher retention ratio.
When a company has taken too much debt, it may retain cash to pay the debt and thus improve its financial risk profile.
Capital intensive companies like automobiles, oil production & refining, telecommunication, etc requires large amount of funds to maintain their level of production. So, this type of industry calls for higher retention ratio.
The ratio also gets influenced by the company’s earnings volatility and its dividend payment policy.
What are the limitations?
The ratio does not always indicate a good financial health of a company. Companies with lower earnings may pay less or no dividends to its shareholders, thus resulting in a higher retention ratio.
The ratio does not indicate whether the company is reinvesting the retained funds back into the company or not.
The ratio also fails to capture whether the retained capital has been reinvested and whether such reinvestment is done effectively and efficiently.
Key Takeaways
Retention ratio is a fundamental analysis ratio that indicates the amount of profit that is retained back into the business for future growth of the business. It increases the retained earnings of the company.
Investors may prefer capital appreciation over dividend payments, if the company has high growth potential.
The ratio helps to demarcate between defensive and cyclical stocks. Defensive stocks usually do not encounter earnings volatility and thus have stable payout ratio than cyclical stocks, whose earnings are volatile.
The ratio, just like any other, should not be studied alone but in conjunction with other financial ratios. Moreover, it should be observed over a period of time to rightly evaluate the performance of the company.
Visit StockEdge to avail carious technical scans and reports of Stock Markets.









I am constantly thought about this, regards for putting up.
I am impressed with this web site, really I am a fan.