The derivatives market was introduced in India in the year 2000, and since then, it has been gaining great significance, just like its counterpart abroad.
Just like shares, Derivatives are also traded in stock exchanges. Derivatives are a type of security whose value is derived from an underlying asset.
These underlying assets can be stocks, bonds, commodities, or currencies. The popularity of derivatives trading can easily be understood by the daily turnover in the derivatives segment on the exchange, which is much higher than the turnover in the cash segment on the same exchange.
- What is Derivatives Trading?
- Difference between Cash Market and Derivative Market
- Terms used in Derivatives Trading
- What are the types of Participants in the Derivatives Market?
- Types of Derivatives Contracts
- Difference between Forward and Futures Contracts
- Different Types of Futures Contracts
- What are the types of Indicators used in Derivatives Trading?
- Types of Margins
- You can also watch our video by Mr Vivek Bajaj
- Bottomline
What is Derivatives Trading?
Derivatives can either be exchange-traded or traded over the counter (OTC). Exchange refers to the formally established stock exchange wherein securities are traded and have a defined set of rules for the participants.
Whereas OTC is a dealer-oriented market of securities, an unorganized market where trading happens by phone, email, etc. Derivatives traded on the exchange are standardized and regulated.
On the other hand, OTC derivative constitutes a greater proportion of derivatives contracts, but it carries higher counterpart risk and is unregulated. These financial instruments help in making a profit by simply betting on the future value of the underlying asset.
Hence the name derivative as they derive the value from the underlying asset.
For instance, Derivative contracts are used by wheat farmers and bakers in order to hedge their risk.
The farmer fears that any fall in price would impact his income. Hence enters, the contract to lock in the acceptable price for the given commodity. On the other hand, the baker, in order to hedge his risk on the upside, enters the contract so that he does not suffer losses with a rise in price.
Derivative contracts like futures and options trade freely on exchanges and can be employed to satisfy a variety of needs which includes the following-
1. Hedge your securities
The derivative contracts can be used to hedge your securities from price fluctuations.
The shares which you possess can be protected on the downside by entering into derivatives contracts. Moreover, it also protects you from the rise in the share price which you plan to purchase.
2. Transfer of risk
This is the most important use of derivatives, which helps transfer risk from risk-averse people to risk-seeking investors.
The risk-seeking investor can enter into risky contrarian trades to gain short-term profits. While the risk-averse investor can enhance the safety of their position by entering into derivatives contracts.
3. Benefit from arbitrage opportunities
Arbitrage trading simply means buying low in one market and selling high in another market.
So with the help of derivatives contracts, you can take advantage of price differences in two markets. Thus it helps in creating market efficiency.
Lets start off by understanding Derivatives basics.
Difference between Cash Market and Derivative Market
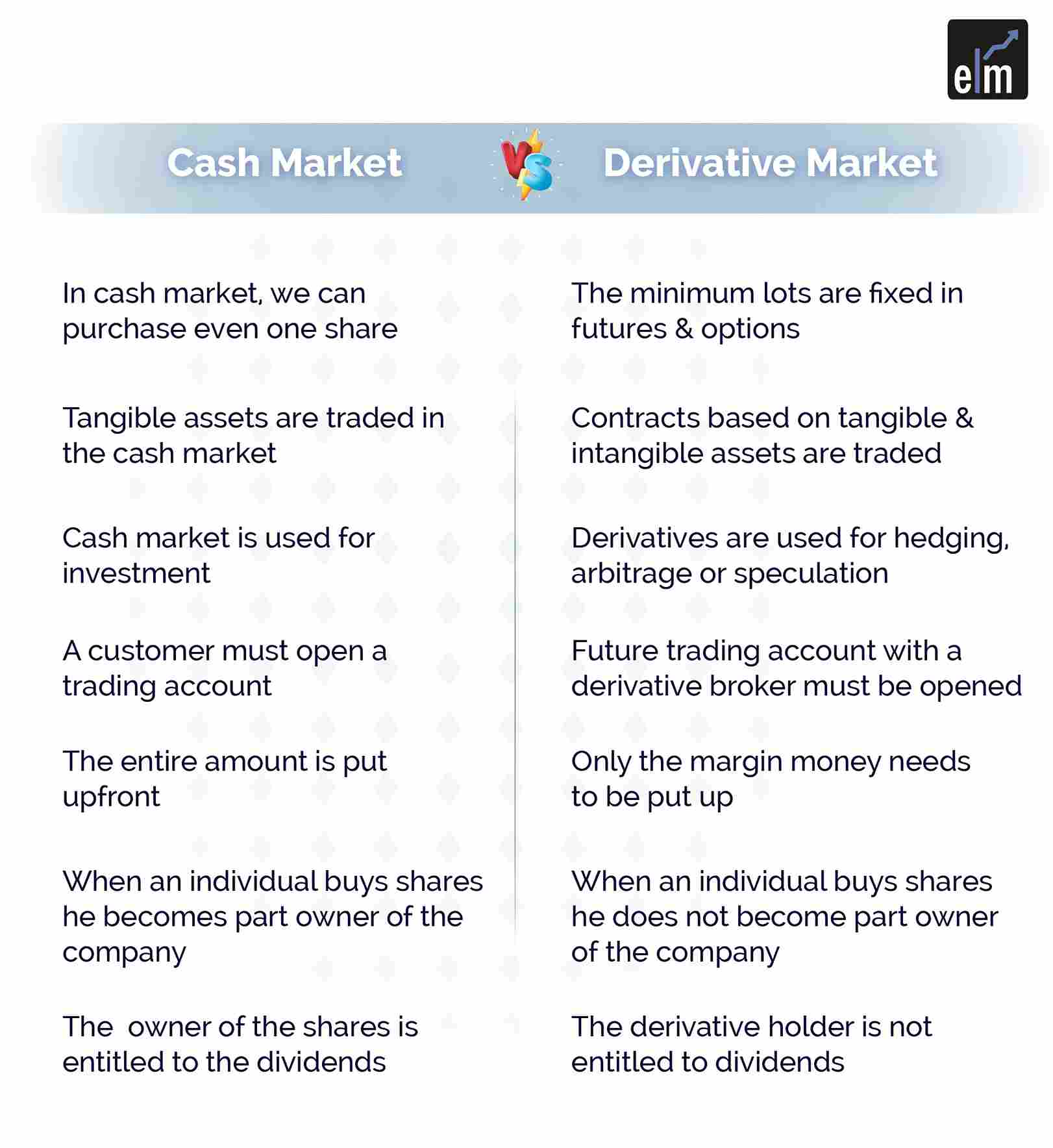
In the cash market, we can purchase even one share, whereas, in the case of futures and options, the minimum lots are fixed
In the cash market, tangible assets are traded, whereas derivatives contracts based on tangible or intangible assets are traded.
The cash market is used for investment. Derivatives are used for hedging, arbitrage, or speculation.
In the case of the cash market, a customer must open a trading and demat account, whereas, for futures, a customer must open a futures trading account with a derivative broker.
In the case of the cash market, the entire amount is put up upfront, whereas, in the case of futures, only the margin money needs to be put up.
When an individual buys shares, he becomes part owner of the company, whereas the same does not happen in the case of a futures contract.
- In the case of a cash market, the owner of shares is entitled to dividends, whereas the derivative holder is not entitled to dividends.
Terms used in Derivatives Trading
Let us understand the most common terminology which is associated with the derivatives market:
- American Style Options– Unlike European Style Options, which can only be exercised at expiration, American Style Options can be exercised at any time.
- At-the-Market– A type of financial transaction in which the buy or sell order is carried out at the going rate on the market.
- At-the-Money- An option with a strike price equal to the current market value in the cash spot market is said to be “at the money.”
- At-the-Money Forward-A forward market option with a strike price equal to the current market price.
- Call Options– This type of financial agreement gives the owner the right, but not the obligation, to purchase a certain quantity of the underlying financial instrument at a certain price with a certain maturity date.
- Commodity Swap: A contract in which counterparties agree to exchange payments related to indices, at least one of which is a commodity index.
- Currency Swap: A currency swap involves the exchange of an interest in one currency for the same in another currency.
- Delta: The change in the financial instrument’s price to changes in the price of the underlying cash index.
- Equity Swap: A contract in which counterparties agree to exchange payments related to indices, at least one of which is an equity index.
- European Style Option: An option that can be exercised only at expiry as opposed to an American Style option
- Forward Contracts: An over-the-counter obligation to buy or sell a financial instrument that is settled privately between the two counterparties.
- Futures Contracts: An exchange-traded obligation to buy or sell a financial instrument.
- Gamma: The degree of curvature in the financial contract’s price curve to its underlying price.
- Hedge: A transaction that offsets an exposure to fluctuations in financial prices of some other contract or business risk.
- In-The-Money Spot: An option with positive intrinsic value with respect to the current market spot rate.
- In-The-Money-Forward: An option with positive intrinsic value with respect to the current market forward rate.
- Option: The right but not the obligation to buy (sell) some underlying cash instrument at a specific rate on a particular expiration date.
- Put Option: A put option is a financial contract giving the owner the right but not the obligation to sell a particular amount of the underlying financial instrument at a pre-set price.
- Spot: The price in the cash market for delivery using the standard market convention.
- Strike Price: The price at which the holder of a derivative contract exercises his right.
- Theta: The sensitivity of a derivative product’s value to changes in the date, all other factors staying the same.
What are the types of Participants in the Derivatives Market?
The participants in the derivatives market can be segregated into three categories, namely-
1. Hedgers
These are traders who wish to protect themselves from the risk or uncertainty involved in price movement. They try to hedge their position using options strategies by entering into an exact opposite trade and passing the risk to those who are interested in bearing the same.
By doing this, they try to get rid of the uncertainty associated with the price. For example, you have 1000 shares of XYZ Ltd., and the CMP is Rs 50. You are planning to hold the stocks for 6-9 months and expect a good upside.
However, in the short term, you feel that the stock might see a correction, but you do not want to liquidate your position today as you expect a good upside soon.
For example, you can enter into an options contract (a part of the derivative strategy) by paying a small price or premium and reducing your losses.
Moreover, it would help you benefit whether or not the price falls. This is how you can hedge your risk and transfer it to someone willing to take the risk.
2. Speculators
They are extremely high-risk seekers who anticipate future price movements hoping to make large and quick gains.
The motive here is to take maximum advantage of the price fluctuations. They play a key role in the market by absorbing excess risk and providing much-needed liquidity when normal investors don’t participate.
3. Arbitrageurs
Arbitrage is a low-risk trade involving buying securities in one market and selling it in another.
This happens when the same securities are trading at different prices in two different markets. For instance, say the cash market price of a share is Rs 100, and it is trading at Rs 110 per share on the futures market.
An arbitrageur observes the same and buys 50 shares @ Rs 100 per share in the cash market and simultaneously sells 50 shares @Rs 110 per share, thus gaining Rs 10 per share.
Types of Derivatives Contracts
Four types of derivative contracts include forwards, futures, options, and swaps. We’ll focus on the first three since swaps are complex instruments we cannot trade in the stock market.
1. Forward contracts
They are customized contractual agreements between two parties where they agree to trade a particular asset at an agreed-upon price and at a particular time in the future.
These contracts are not traded on an exchange but privately traded over the counter.
2. Futures contracts
These are the standardized versions of the forward contract, which takes place between two parties where they agree to trade a particular contract at a specified time and at an agreed-upon price.
These contracts are traded on the exchange.
3. Options
Options is an agreement between a buyer and a seller which gives the buyer the right but not the obligation to buy or sell a particular asset at a later date at an agreed-upon price.
Difference between Forward and Futures Contracts
The main difference between forward and futures contracts are:

Forward contracts are traded on a personal basis, while future contracts are traded in a competitive arena.
Forward contracts are traded over the counter, whereas futures are exchange-traded.
Forward contracts settlement takes place on the date agreed upon between the parties, whereas futures contracts settlements are made daily.
The cost of forward contracts is based on the bid-ask spread, whereas futures contracts have brokerage fees for buy and sell orders.
In the case of forwards, they are not subject to marking to market. On the other hand, futures are marked to market.
Margins are not required in the case of a forward market, whereas in futures, the margin is required
In a forward contract, credit risk is borne by each party, whereas in the case of futures, the transaction is a 2-way transaction; hence both parties need not bother about the risk
Different Types of Futures Contracts
Different types of futures contracts are available for trading depending on the underlying asset.
They are: –
1. Individual stock futures
They are contracts between 2 investors. The buyer promises to pay a specified price for 500 shares of a single stock at a predetermined future point.
The seller promises to deliver the stock at a specified price on a specified future date.
2. Stock index futures
The underlying asset is the stock index. Stock index futures are more useful when one is speculating on the general direction of the market rather than the direction of an individual stock.
It can be used for hedging a portfolio of shares.
3. Commodity futures
Here the underlying asset is a commodity like gold, silver, nickel, crude oil, etc.
In India, commodity futures are traded on 2 exchanges: MCX, i.e., Multi Commodity Exchange, and NCDEX, i.e., National Commodities and Derivatives Exchange.
Examples of commodities are pulses, cereals, fibre, oil and seeds, energy, metals, and bullion.
4. Currency futures
These exchange-traded futures contracts specify the price in one currency at which another currency can be bought or sold at a future date.
These are legally binding, and the parties that hold the contracts on the expiry date must deliver the currency amount on the specified date at the specified price.
5. Interest rate futures
In this case, the underlying asset is the debt obligation which moves according to the changes in the interest rates.
What are the types of Indicators used in Derivatives Trading?
Below are 3 types of indicators used in Derivatives Trading:
1. Put-Call Ratio
The put-call ratio is one such market sentiment indicator used in the derivatives market. A ‘Put Option’ contract is one where we agree to sell an underlying asset in the future; on the other hand, a ‘Call’ contract is one where we agree to buy an underlying asset in the future at a fixed rate.
The put-call ratio is measured by dividing the number of put contracts in the derivatives market by the total quantity of call contracts. One should note that the Higher the number, the greater the chances of selling in the future, which may lead to a fall in stock prices.
If you are not familiar with these terms then we recommend you do our Options Trading Course.
So, a rising put-call ratio, or a ratio that is greater than .7 or 1, means that traders are buying more puts than calls indicating that bearish sentiment is building in the market. On the other hand, a falling put-call ratio below .7 and .5 is considered a bullish indicator, meaning more calls are being bought than puts.
This indicator can also be taken as a contrarian indicator. Contrarian traders use the put-call ratio to determine when traders are getting overly bullish or too bearish. So, an extremely high put-call ratio means the market is extremely bearish. To a contrarian trader, that can be a bullish signal as it indicates that the market is extremely bearish and may reverse.
On the other hand, an extremely low ratio may indicate that the market is extremely bullish, and contrarian traders may conclude that the market is too bullish and may reverse to the downside.
2. Open Interest
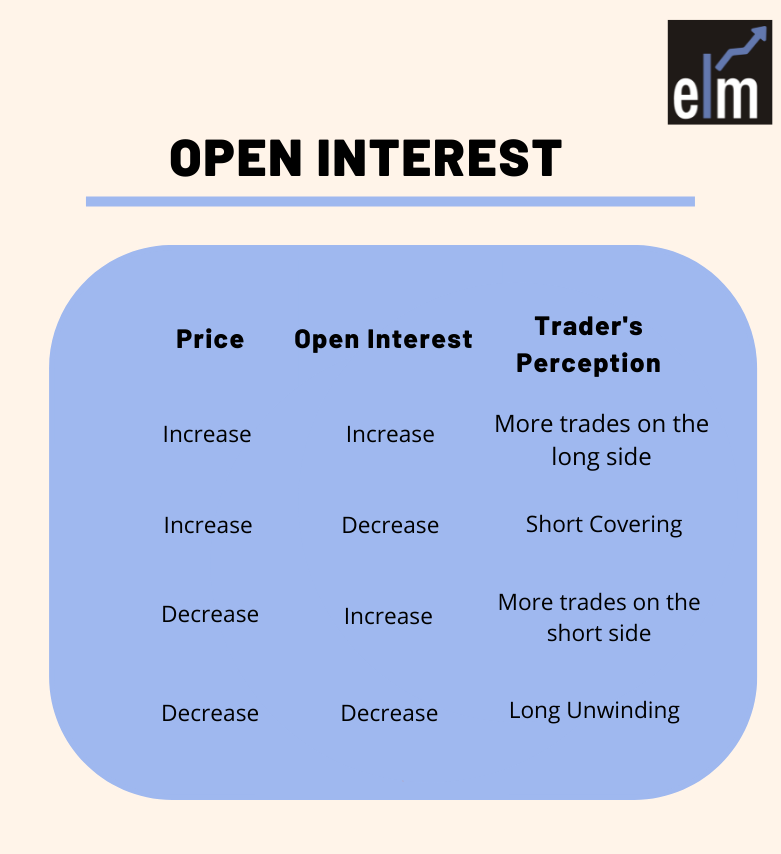
Open Interest refers to the total number of futures contracts or options that are held by traders at any particular moment. Open interest is known to be one of the best sentiment indicators and also for understanding the reliability of price movements.
So let me first explain how the open interest in the market is formed. There must be a buyer for every seller and vice-versa to make up an open interest contract. So, when buyers and sellers enter one new position, open interest is increased, and when the same buyer and seller decrease their position, open interest is reduced.
Open interest increasing means fresh money is flowing into the market, and a decrease in open interest suggests money outflow from the market. Buyers move the market up by investing fresh cash into the market, while the seller does the opposite. Open Interest increases when the fresh contract exchanges hands.
Below is the table that will help you understand how the change in open interest indicates the future direction of the index or stocks:
3. Vix
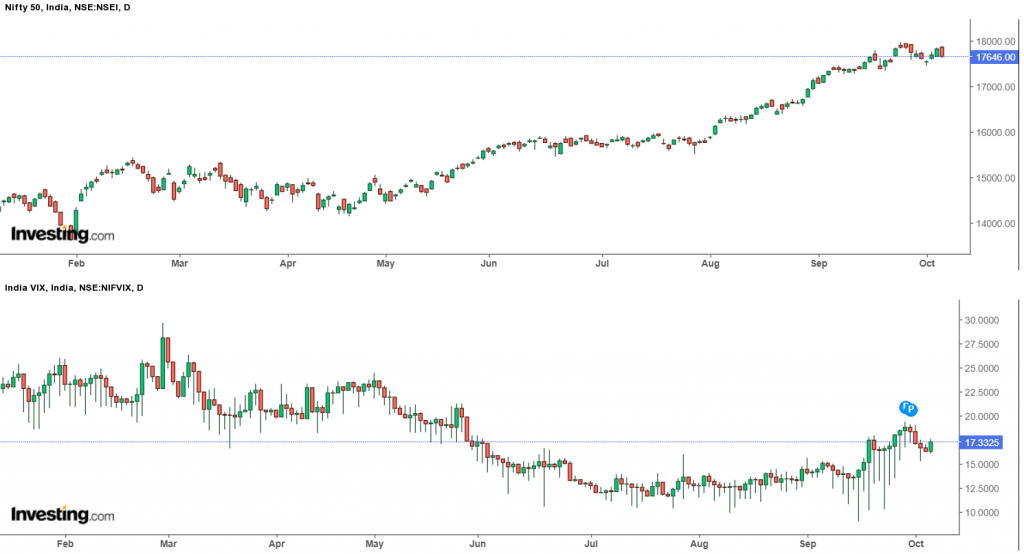
Vix is again an important sentiment indicator as it gauges fear, uncertainty and volatility in the stock market. We all know that the stock market is known for its volatility
When the volatility is high, it means there will be a greater change in stock prices. The volatility of the National Stock Exchange is measured by the VIX India index, which is calculated based on the prices of Nifty Options contracts in the derivatives market.
This indicator is also called the fear gauge because it indicates an increase in risk when the VIX shoots up. Generally, a rise in the VIX indicates a fall in the market which can be seen from the chart below:
Types of Margins
There are basically three types of margins in derivative trading. These are the Initial margin, Maintenance margin, and Variation margin-
1. Initial margin
You must deposit the initial cash in your account before you start trading. This is required to ensure that the parties honour their obligation and provides a cushion to the losses in the trade.
In simple words, it is like the down payment for the delivery of the contract.
You can also read more from Derivatives Module in ELM School
2. Maintenance Margin
It is a cash balance that a trader must bring to maintain the account, as it may change due to price fluctuations. The maintenance margin is a certain portion of the initial margin for a position.
If the margin balance in the account goes below such margin, the trader is asked to deposit the required funds or collateral to bring it back to the initial margin requirement. This is known as a margin call.
3. Variation Margin
As soon as the margin falls below the maintenance margin, you must deposit cash or collateral to return the account to the initial margin.
Want to learn more about derivatives and interested in making career? Join our derivative analyst course now
You can also watch our video by Mr Vivek Bajaj
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are derivatives markets important?
Derivatives are very as they not only help investors to hedge their risks but also help in global diversification and hedging against inflation and deflation.
What is an example of a derivatives market?
For example, Derivative contracts are used by wheat farmers and bakers in order to hedge their risk. The farmer fears that any fall in price would impact his income Hence enters the contract to lock in the acceptable price for the given commodity.
On the other hand, the baker, in order to hedge his risk on the upside, enters the contract so that he does not suffer losses with a rise in price.
What is the difference between the spot market and the derivatives market?
The spot market trades financial instruments, such as commodities, currencies, and securities, directly for delivery. On the other hand derivatives market is based on the delivery of the underlying asset at a future date
What is the need for a derivatives market?
The main purpose of derivatives is to reduce and hedge risk.
Bottomline
We hope you found this blog informative and use the information to its maximum potential in the practical world. Learn more about trading in derivatives from our online trading course. Also, show some love by sharing this blog with your family and friends and helping us spread financial literacy.
Happy Investing!
For stock related queries visit web.stockedge.com









That is a good tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere.
Simple but very precise information… Thank you for sharing this one.
A must read post!
Very Informative !!
Hi,
We are glad that you liked our blog post.
Thank you for Reading!
Such an informative!!!
Hi,
We really appreciated that you liked our blog.
Keep Reading!
The article you have shared is amazing info!
Hi,
We really appreciated that you liked our blog!
Thank you for Reading!
Keep Reading!