Introduction to Banking
Banking
Banks are an integral part of our life. Whether it is about sending money to someone or receiving the payments, or for instance, taking a home loan or a car loan, the banks play a pivotal role in all financial transactions. So, to make you understand the banking system, let's share a story of a young man named Sathish.
Satish was delighted to get the appointment letter for a job in a prestigious software company after completing his engineering. It was a tough interview and he was the only student from his college who got through.
Upon meeting the HR, he got the pre-joining forms, one of which needed his bank account details. Being a student, he did not have any bank account. His father has a wholesale business with all dealings in cash. He has never had a bank account because he believes his money will remain safe with himself rather than with someone else. Since childhood, Satish has seen safe boxes in his house stashed with cash. So for him, the concept of a bank account was rather alien.
On his way back, Satish walked into the bank at the corner of his neighborhood and asked the helpful lady at the counter to explain to him all about a bank account. The lady was eager to help and clarified everything he needed to know.
What is a Bank account and why is it needed?
A bank account is a financial account maintained by the bank on behalf of a customer. It is an arrangement whereby a customer can deposit and withdraw money, in a physical form or in a digital form. By opening a bank account, a customer entrusts the bank to keep his/her money safe.
A bank account serves a lot of purposes to everyone. The three most important ones include:
- Safety: Banks provide safety to customers. Keeping large amounts of cash at home is susceptible to risks such as stealing or fire. However, banks are safe and well regulated. A certain amount of money is automatically insured against loss by the Government. Even if a bank is robbed or goes bankrupt, customers receive the insured amount.
- Convenience: Handling a bank account is very easy. All payments can be made through cheque or online transfer and money can be withdrawn through a debit card or from the branch itself.
- Savings: Bank accounts help in developing a habit of savings among individuals. Bank accounts are of various types, some of which pay interest. Instead of keeping cash idle at home, keeping it in the bank can help make the money grow.
Types of bank accounts in India
Next, Satish wanted to know what are the different types of bank accounts to decide which one would suit him.
The lady at the bank explained that truly speaking, bank accounts are of two types:
1. Deposit Accounts
2. Loan Accounts
Deposit Accounts are accounts where customers deposit money at a bank. In return, the bank may or may not pay interest on the money. (We will discuss more on ‘Deposit accounts’ in the next unit).
Loan Accounts, on the other hand, are accounts where a bank lends money to customers. The bank charges a certain amount of interest from the customers in lieu of such lending.
We will discuss more on Deposit and Loan accounts in our subsequent units.
Deposit Accounts
Let us start with Deposit Accounts. They are mainly of three types:
Savings Bank Accounts:
As the name suggests, these accounts are designated to help people save money. People can deposit money in these accounts, which earn an annual rate of interest. The Reserve Bank of India (regulatory body of the Indian Banking system) provides guidance on the rate of interest that the banks can offer, however, each bank uses its own discretion to decide the rate of interest that it will offer to its customers.
Below are the savings bank account interest rates of some Indian banks as on Jan 2022.

Upon opening a savings bank account, customers receive cheque books and debit cards to carry out transactions on these accounts. Depending on the nature of the account, the bank provides other facilities such as internet banking, mobile banking, and more. It can be opened by individual customers, associations, clubs, organisations and others. It is also possible that two or more people can jointly open a savings account as well.
Most banks have a wide range of savings account offerings for their customers. This allows customers to choose the kind of account that suits their needs.
For example, Kotak Mahindra Bank has fifteen different kinds of savings accounts tailor-made to suit customer needs. From savings accounts specifically designed for women and children to accounts designed for a digitally inclined customer, the wide range of offerings makes the bank’s saving account products extremely popular.
Current Accounts:
The nature of banking requirements differs considerably between different kinds of users. Businesses need to deposit and withdraw cash regularly, sometimes several times a day. This results in a continuous movement of money in business accounts. Moreover, businesses need facilities such as overdrafts, remittances, and others that individuals may not require. This is where a Current Account comes in. These accounts are offered to business entities so that they can conduct their business transactions with ease. No interest is paid by the bank on the money deposited in a current account. A current account can be opened by limited companies, partnerships, proprietorships, religious institutions, educational institutions, and any entity which needs such services. Current Accounts can also be opened by individuals singly or jointly. However, considering current accounts don't pay any interest, it is not a popular option among individual customers.
Different businesses have different kinds of needs which can vary considerably from each other. Hence, most banks have a range of current account offerings for their customers. Kotak Mahindra Bank offers ten different kinds of current accounts for its customers, which vary in features. Ranging from a Startup Regular Current Account to an Elite Current Account, the bank's offerings cover a wide range of business requirements.
Fixed Deposits:
These are deposits where customers pledge to keep a certain sum of money with the bank for a certain time period, and the bank, in turn, promises to pay them a fixed sum of money as a return. Fixed deposits can be created for a time period as low as seven days to as high as ten years. The percentage of interest depends on the time period for which the money is fixed with the bank. The rates of fixed deposits for the same tenure may vary from one bank to another. Traditionally, fixed deposits have been the most popular way of saving money in India.
More on Fixed deposits have been discussed in detail in the upcoming units of this module.
Loan Accounts
Next, let us discuss Loan Accounts.
As the name suggests, loan accounts are those where a bank lends money to its customers and charges a certain interest in return. Sometimes these loans are provided for a specific purpose such as a home loan to buy a house, car loan to purchase a car or sometimes they are provided with no specific intention in mind such as a personal loan. Loans have been explained in detail in Unit 6 of this module.
Common Guidelines for Opening and Operating Bank Accounts:
Continuing with our previous example of Satish, now that he had a basic knowledge of bank accounts, he wanted to know what he needed to do to open an account.
The lady at the bank explained to him that to open a savings bank account, one needs to provide the following documents:
- Identity proof such as Aadhar card, PAN card, or Passport.
- Address proof such as Aadhar card or Passport or Voter ID card or Utility Bill.
- A photo
With the help of the above documents, a bank account can easily be opened. In case of the non-availability of any such document, the bank representative will suggest documents required as per the rules and regulations of the Indian banking system.
With the help of the above documents, a bank account can easily be opened. In case of the non-availability of any such document, the bank representative will suggest documents required as per the rules and regulations of the Indian banking system.
In the case of opening current accounts, customers will need to submit documents of their business. The required documents also depend upon the nature of the business entity.
Original copies of all the documents have to be shown to the bank representative, and the signed photocopies of the same are required to be submitted.
Banks also offer nomination facilities where-in customers can designate someone to inherit the money in case of his/her demise. This facility should always be exercised, especially if there is only one holder in the bank account. The nomination facility is available for individual customers only. The nomination facility has been discussed in detail in the upcoming modules.
Mistakes To Avoid While Opening A Bank Account
Now that we know what things are required to open a bank account. Let us discuss a few common mistakes that one should avoid while opening a bank account.
Admit it, most people often take account opening too lightly and end up making mistakes which turn out to be harmful in the long run. Here are a few guidelines that one should follow:
- Customers should always provide an authentic document while opening a bank account. The bank conducts due diligence from time to time. If any document is found to be forged, the bank can freeze the account, in which case the money in the account will become unusable.
- Customers should ensure the name in the account matches the customer's original name. A difference of even a letter can be harmful.
- Often the bank representative volunteers to fill up the account opening forms. Customers should always check the filled out form before final submission and ensure all the information provided is correct.
- Customers should never sign a blank document.
Operating a Bank Account
While operating a bank account is easy, a few things need to be kept in mind:
- Most banks require customers to maintain a minimum/average balance in the account. If this is not maintained, a charge is deducted.
- Customers can deposit money in their account either at the branch or at cash deposit machines.
- Money can be withdrawn from the account through ATM machines or through bank branches.
- Customers can transfer money to other persons using cheque or through online transfer modes such as NEFT, IMPS, RTGS, etc.
- Online Banking is the most convenient way to operate a bank account. It is like a mini-branch available online where customers can perform almost all transactions.
- The bank provides a statement of account or bank passbook updated at regular intervals. This helps customers to keep a track of the transactions in the account.

Different Options for Operating a Bank Account:
'Mode of operation' is a term commonly used with regard to bank accounts. It refers to how a bank account is operated. As mentioned earlier, any account can be opened by an individual alone or together with two or more individuals. When there is more than one account holder, customers can choose different kinds of modes of operation such as single, either or survivor and jointly. When there are two holders in an account and any one of the holders can perform financial transactions in an account independently, then the mode of operation is known as 'Either or Survivor'. In case there are more than two holders, this mode of operation is called 'Anyone or Survivor'. Customers can also stipulate a clause where unless two holders sign together, a transaction cannot be carried out in the account. This mode of operation is known as 'Jointly'.
Traditionally, bank accounts were operated from the bank branches. However, with the advent of digital technology, things have become easier. People can operate their bank accounts anywhere anytime using their computer or mobile. However, to do so, it is imperative to sign up for internet banking and mobile banking facilities. We will discuss more on internet banking services offered by the banks in the upcoming section of this module, but before that, let us learn how to select a suitable bank account as per our needs in the next unit.
Selecting A Suitable Savings Bank Account
In India, Banking has gone through enormous changes, especially in the last decade. Today, the number of banks, as well as the products they offer, is vast. There are so many choices that the job of choosing any one bank and the type of savings account is extremely difficult for an individual.
Below are a few things to consider while choosing the right savings account:
Average balance requirement:
As mentioned earlier, an average balance has to be maintained in savings bank accounts. The stipulated amount, however, varies from one bank to another. While choosing a savings account, customers need to check this stipulated amount and consider the one which they are comfortable to maintain in the long run.
Interest rates:
Different banks offer different interest rates on savings accounts. The rate may vary as per the savings account type as well as the amount of money kept. Hence, this should be an important consideration.
Online and mobile banking:
Online and mobile banking have become a necessity in today's world. The stronger the online platforms, the less cumbersome it will be to operate an account. Customers must have a look at the online platform of different banks and choose a robust one. Moreover, the kind of transaction that can be done online may vary depending on the type of savings account. Having more options online is always better for ease of operation.
Services and fees:
The services and fees of different banks are different. In fact, the services and fees of different kinds of savings accounts of the same bank may be different. It is an important factor to look into.
Branch and ATM network:
For deciding the right bank to open a savings account, it is essential to look into the branch and ATM network. While it is right that customers can withdraw money from an ATM, however, using other bank ATMs might attract some charges.
Fund based and Non Fund based services
As we discussed earlier, banks in today's world offer a vast number of products to their customers. Similarly, they also offer a whole host of services as well. The services can be divided into two categories -
- Fund based services.
- Non-fund based services.
Fund based services are those where banks provide short and long term funds to individuals and businesses. The financing is provided based on the repayment power of an individual or a business. These are basically different types of loans offered by banks.
Non-fund based services or fee-based services, on the other hand, are those where banks operate certain functions and earn a fee out of the same. This fee can be in the form of dividends or brokerages or a commission.
Types of fund based services offered by banks to individuals:
Banks offer a variety of fund based services to individuals which help individual customers to fulfil their dreams and aspirations.
The most common ones include:

The rates of interest and the tenure for different loans are different. While in most cases customers pledge collateral with the banks (such as a house in case of a home loan), some loans may not involve a collateral (such as a personal loan).
Types of fund-based services offered by banks to businesses:
Most banks also offer a range of fund-based services to businesses. From setting up a business to expanding it, these loans are provided for a variety of purposes. They help in establishing, running, and expanding a business.
The most common kinds of loans provided to businesses include:
- Lease financing
- Hire purchase
- Consumer credit/consumer finance
- Factoring
- Venture capital financing
- Housing finance
Customers have to submit documentation as stipulated by the bank to obtain fund-based services. Upon evaluating a customer's repaying power, a bank decides whether it will provide the loan. The decision of approving a loan is solely at the discretion of the bank.
From trading and demat accounts to market monitoring and analysis—equip yourself with essential basic finance skills
Types of non-fund-based services offered by banks to individuals and businesses
Banks offer a wide-range of non-fund based services to individuals as well as businesses. Some of these include:
- Credit cards
- Debit cards
- Smart cards
- Safe deposit lockers
- Cheque
- Demand draft
- Insurance
- Mutual Funds
- Financial products issued by other financial institutions
These non-fund based products offer convenience to customers as well as help them invest their funds in different avenues.
By the end of the discussion, Satish had an idea of not only what account he wants to open, but also what banking is all about. He was now determined to go home and research the different aspects he just learned.
Embark on your finance journey with our finance courses beginner. Explore Bank's Fund and Non-Fund Services essentials. Enroll now for foundational knowledge!
Fixed Deposits
It’s been three months since Satish has started working and has opened a savings bank account where his salary is credited every month. Satish has been able to save some money and wants to invest the fund to earn some returns. However, this being his first savings, he does not want to risk the fund and is looking for an option where his money would be secure.
Satish searched the internet and started reading about Fixed Deposits.
So, what is a Fixed Deposit?
A Fixed Deposit, more commonly referred to as an FD, is an investment account held with the bank where the bank promises the investor to pay a fixed rate of interest for a certain time period. The condition to obtain the interest amount is that the money should remain with the bank for a mutually agreed period of time.

Features of Fixed Deposits
Fixed Deposits are a safe investment option since the investment amount i.e. the principle remains secured.
The time period for which a fixed deposit is made may vary. In India, customers may choose to invest their funds for as low as 7 days to as high as 10 years.
- The rate of interest on fixed deposits varies from one bank to another.
- The rate of return paid by the bank on a fixed deposit depends on the time period for which the money has been fixed.
- The return on fixed deposit, though calculated annually, is paid monthly or quarterly.
- The interest amount can be taken by the customer monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, annually, or upon maturity of the fixed deposit.
- In case customers do not withdraw the interest before the maturity of the fixed deposit, the monthly or quarterly return is reinvested, yielding a higher return for the customer. This is known as cumulative interest.
- In most cases, fixed deposits can be withdrawn prior to the maturity date. This process is known as the premature withdrawal of fixed deposits. However, a penalty has to be paid for premature withdrawal.
- Some banks offer loan facility against fixed deposits.
Interest Calculation on Fixed Deposits
Fixed Deposit interest is calculated based on the formula provided below:
M=P(1+ r/m)mn
Where,
M = Maturity Amount
P = Deposit Amount
m = Frequency at which interest is compounded in an year
n = Number of Years
r = Rate of return (%)
Auto-Renewal of Fixed Deposits
Most banks offer an auto-renewal facility on fixed deposits. In the case of auto-renewal, the customer authorizes the bank to automatically reinvest the money upon the maturity of a fixed deposit. Hence, a new fixed deposit is automatically created upon the maturity of the old one.
Tax on Fixed Deposits
According to the Interim Budget 2019-2020, fixed deposit interests are fully taxable at the slab rate. In case the interest on all fixed deposits held by a customer in the same branch of a bank exceeds ₹40,000 in a year, then Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is deducted by the concerned bank. For senior citizens, this limit is ₹50,000. The rate of TDS is 10% for resident Indians and 30% for Non-Resident Indians. The rate will be 20% for resident India if he/she has not provided their PAN to a particular bank. In case the income from all sources of a resident Indian is less than Rs 2.5 lakhs per annum, then he/she can submit Form 15 G to inform the bank to not deduct TDS. In the case of senior citizens, Form 15 H has to be submitted.
Ready to dive into the A2Z of Finance? Enroll now and master the essentials of banking, including fixed deposits!
Recurring Deposit
As Sathish learned more about Fixed deposits, he came to know that there are two ways to invest money in fixed deposits- as a lump sum or a fixed amount monthly. Recurring deposits are fixed deposits where customers can invest a fixed sum of money every month. The money can be debited from a savings/current bank account on a fixed date every month. Recurring deposits offer customers a chance to build up a savings corpus. It also brings a habit of investment in people. In most cases, recurring deposits can be made for a period of 6 months to 10 years.
When a recurring deposit is opened, the maturity value is indicated assuming the customer invests the fixed sum for the fixed deposit term agreed upon. Some banks provide loans on recurring deposits.
Fixed Deposits vs Recurring Deposits
Below is a comparison of the features of Fixed Deposits and Recurring Deposits:

Different Types Of Fixed Deposits In India
Apart from the types of fixed deposits, we have learned in earlier units. There are a few more different types of FDs available. In India, Fixed Deposits are a popular investment choice. In general, the following types of Fixed Deposits are offered by banks in India:
Regular Fixed Deposits
This is the vanilla fixed deposit where the money is deposited for a fixed tenure and the bank pays a certain rate of interest. The customer has the option to choose the interval at which he/she will withdraw the return.
Recurring Deposits
In this deposit, the customer deposits a fixed sum of money every month for a predetermined period of time. The bank pays a rate of interest to customers in return.
Tax Saving Fixed Deposits
These are specialized Fixed Deposits where the principal amount gets a tax exemption. The principal amount is locked for five years. A premature withdrawal facility is not available on these kinds of deposits.
Senior Citizen Fixed Deposits
These Fixed Deposit schemes are for people above 60 years of age. They attract an additional rate of interest since a customer’s source of income is limited post-retirement.
Sweep-in Fixed Deposits
This is a kind of fixed deposit that gives a savings account holder freedom to enjoy greater returns. In this kind of deposit, the account holder can designate a limit in his bank account. When the balance in the account goes above the limit, a fixed deposit is automatically created so that the fund earns higher returns. Similarly, when the balance in the account goes below a certain amount, the fixed deposit automatically breaks and the money is swept back to the account. This is a special kind of fixed deposit which is offered by only certain banks such as Kotak Mahindra Bank.
Deposit Insurance System
Having read all the above information, a very logical and common question that came to Satish’s mind is what will happen to his money if the bank becomes bankrupt. Upon exploring the internet, he learned about the 'Deposit Insurance System' and was relieved to learn more about it.
A Deposit Insurance System is a system established by the Government to protect customers against the loss of the money deposited with a financial institution in case the latter becomes insolvent. This is done through RBI’s subsidiary Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) of India which ensures deposits of all banks including fixed deposits, current and savings accounts up to a limit of ₹500,000 for each depositor. The insurance cost is borne by the respective banks.
In case a bank covered by the Deposit Insurance Scheme of DICGC fails or is merged with another bank or undergoes liquidation, the DICGC pays the amount due to depositors. At present, the DICGC covers all commercial and cooperative banks of India, except a few.
However, the maximum insured amount per depositor is ₹ 5 Lakhs including principal and interest. Therefore, if a person has deposited ₹492,000 and the interest amount due to him is ₹10,000, the depositor will get only ₹500,000 back and will not get the additional ₹2000 due to him. In case a person has different accounts in different branches of the same bank, then all the accounts are consolidated and a total of ₹500,000 is paid to the person.
Circumstances Leading To Closure of Bank Accounts
Previously we learned that DICGC is there to safeguard any loss faced by our banks. But to keep things under check, we also need to be careful. Under normal circumstances, banks will not close any bank account or deposit account. However, the following are some of the circumstances which may lead to such closure that we must avoid.
So, what are they?
Inadequate Know Your Customer (KYC) Documents
It is a customer’s duty to submit up to date documents to banks when asked for. In case the documents are not up to date and even after repeated follow-ups the customer has not submitted relevant documents, then the bank may close an account.
Dormant or Inactive Account
While banks maintain an account, it is the responsibility of the customer to transact in the account and keep it active. In case an account is dormant or inactive and the bank has sent repeated requests to the customer to activate the same, the bank can close an account.
Banks make every effort not to close any account since they value their customers. However, each bank reserves a right to choose their customers, and hence any kind of illegal activity might lead to the closure of an account. In January 2019, an Indian bank closed the account of one of its customers after it was found that the customer had been dealing in Cryptocurrencies. However, things are now much clearer with the introduction of the Crypto Bill in Lok Sabha in the year 2022.
Banking Transaction
Having learned about Fixed Deposits, one day, Satish left his office early to visit the bank and open a fixed deposit. When he met the representative at the counter, he was told that there was no need for him to visit the branch, he could have done it himself if he had signed up for online banking.
Surprised, Satish wanted to know more about it and got to know the following information:
Various Banking Channels for Transactions
Banks offer their services through various channels which help them to serve their customers better. Two decades back, customers could avail of banking services only through branches. Banking has come a long way since. Today, banks service their customers through:
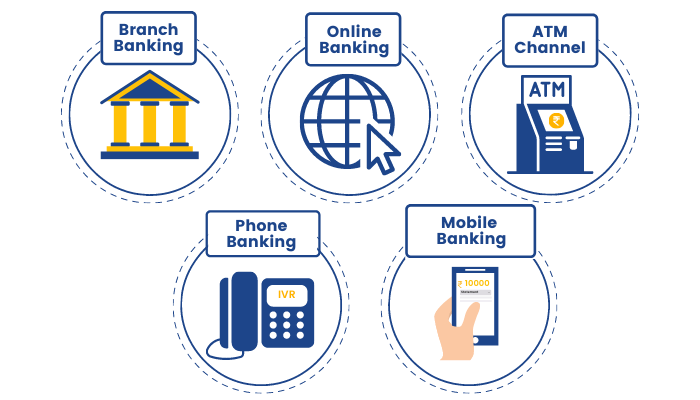
- Branch Banking: This is an office of the bank where all kinds of banking operations and transactions can be done under one roof. This is the most traditional channel. It is manned by trained and knowledgeable bank personnel who are eager to help customers.
Sometimes, banks open a miniature version of branches in some locations to serve their customers. Known as ‘Extension Counters', these are mini branches through which some of the functions of branches can be performed. These extension counters help banks to serve their customers better.
- Online Banking: Almost all banks have a robust Online Banking portal nowadays which are mini branches available online. Customers are issued with their own login ID and a confidential password to access their account. From viewing transactions to making foreign remittances, customers can perform almost all transactions online. They can also make service requests for those services which are not available online and have a bank representative contact them in return.
- ATM Channel: There was a time when people had to make trips to bank branches and wait in long queues to withdraw even ₹ 100 from their accounts. Today, very rarely people visit a bank to withdraw money, thanks to Automated Teller Machines (ATM). Customers can withdraw money 24 hours a day from any ATM located near them. Customers can also deposit money, view recent transactions, express their interest in obtaining a loan or a credit card, and perform a host of functions using ATMs.
- Phone Banking: There's a mini-branch available on customer's phones today which is known as Phone Banking. The Phone Banking channel enables banks to serve their customers through an Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system and representatives over the phone. It is an extremely useful channel for customers and enables them to perform a host of banking activities over the phone.
- Mobile Banking: The whole world is glued to their mobile these days. So it is essential for banks to have a mobile presence as well. Most banks have a functional mobile app through which many transactions can be done.
Branch Banking And Online Banking
Previously as we have learned about various banking channels along with Sathish, in today's modern world, there are two types of banking channels which are extremely popular. They are Branch Banking and Online Baking. Let us discuss them in more detail in this unit and learn the benefits of online banking over branch banking.
Branch Banking
A term often related to banks is Branch Banking. To put simply, Branch Banking refers to all the activities that are carried out within the branch of a bank. This includes things such as cash deposit, cash withdrawal, making demand drafts, processing various documents, obtaining loans, making queries, and others. Branch Banking has gone through tremendous change over the last two decades from the traditional times when a customer had to go to a branch for every small transaction to the current situation when customers are able to transact on an account anytime anywhere.
Online Banking
The worldwide digital revolution has made banking easy for customers. Today, customers can perform almost all kinds of transactions on their account through Online Banking or more popularly called ‘Net Banking’. Online Banking provides someone with the ability to manage funds from a mobile device or a computer. There is no need to visit a branch anymore since Online Banking empowers a customer in almost every way. It is offered to customers free of cost by banks.
Online Banking is a win-win for both customers as well as banks. While it gives customers the convenience of managing the account from anywhere, it also helps banks reduce their cost of operating branches.
Benefits of Online Banking
The benefits of Net Banking are far-reaching, some of which include:
- 24 X 7 availability
- Convenience
- Faster transaction speed
- Variety of transaction options
- Inexpensive option
Transactions Available Through Online Banking
In the last unit, we learned the benefits of online banking. But can it stack against the traditional branch banking in terms of different transactions we can do? Let us find out:
Different banks have different kinds of online banking services. The portal of some is better than the other in terms of functionality, speed, and performance. Customers can perform the following transactions from most online banking portals:
- Transfer Funds: Money can be easily transferred from one bank to another using options such as IMPS, NEFT, and RTGS. The time taken to transfer money varies from instantly in the case of IMPS to usually a few hours in the case of NEFT and RTGS.
- Pay Bills: Online Banking provides a large range of options to pay monthly bills such as electricity bills, mobile bills, cooking gas bills, broadband bills, water bills, and even credit card bills of other banks. Customers can visit the respective service provider and pay using online banking or visit their online banking login ID and pay the bills. They can also link their bills to their net banking login ID so that on the bill due date, the due amount is automatically deducted from the savings account. This system is known as an ‘auto-debit facility’ which refers to a system where customers authorize banks to debit their account for an agreed sum of money automatically.
- Open Fixed Deposits: Customers can check the rates of fixed deposits and open one from the Net Banking portal. There is no requirement to visit a branch and sign documents. The fixed deposit principal and interest are auto-credited to the customer’s account upon maturity.
- Apply for Loans: Customers interested to avail of loans can apply for the same online. Upon receipt of interest, a bank representative contacts the customer and completes necessary documentation. Some banks offer a pre-approved loan amount to customers depending on the transaction history of their account. This is useful to obtain faster approval and disbursement of loans.
- View Account Transactions: Customers can access their account transactions anytime on their online banking. Customers can also download account statements directly from online banking. The time period for which transactions are available varies from one bank to another. In case a customer requires a physical account statement stamped by the bank, the request for the same can also be made through online banking.
- Access Credit Card Details: In case a customer holds a Credit Card from the bank where he/she holds a savings /current account, the same can be linked to online banking. This helps the customer access credit card details and monitor activity.
- Linking of all relationships under a single ID: Customers can link all the banking relationships held with the same bank under a single online banking ID. This way, customers have a single portal to access their entire portfolio including savings/current account, credit card, loans, insurance, mutual funds, and others which translates to hassle-free banking.
How To Start Online Banking
Satish has learned quite a lot about Online banking. He is now ready to get one for him.
Steps to start online banking:
Step 1: Customer visits a bank branch signs up for Online Banking
Step 2: Bank sends the Online Banking ID and password to the client using two different couriers
Step 3: Customer has to log in using the above ID and passwords
Step 4: Customer is required to change the password upon logging in for the first time
Step 5: Customer can now use online banking
Pros and Cons of Using Online Banking:

ATM Transactions
If you remember, in our earlier units, we have discussed various types of banking channels, of which ATM was one of them. In this section, let's find out what an ATM is and how to transact using one of them?
What is an ATM?
Automated Teller Machines (ATM) present a convenient way of withdrawing cash from a bank account using ATM Cards. Their advent has removed the requirement to visit branches and stand in long queues to withdraw or deposit money. Thanks to ATMs, cash is available round the clock which is extremely helpful, especially during emergencies.
Steps to withdraw cash using ATMs

Before collecting the card, the ATM machine asks customers if they want to perform any other transaction. In case it is required, customers can perform other transactions without removing and inserting the card again.
Different Types of Money Remittance Services Offered By Banks
One of the main functions of banks is to provide remittance services to customers. Remittance refers to the act of transferring money from one place to another. This includes both domestic as well as international transfers.
Domestic Transfers
When money is transferred from one account to another where both the accounts are located in the same country, then it is referred to as a domestic transfer. Traditionally, this used to be done through Demand Drafts, Banker's Cheques, and Money Orders. The banking world has gone online for decades now and hence physical cheques are slowly becoming obsolete. Today, money is transferred through modes such as RTGS, NEFT, and IMPS.
- Demand Drafts and Bankers Cheques: These are physical cheques issued by banks in favor of a specific person where the bank agrees to pay a certain sum of money on behalf of its customer. While preparing these cheques, the required sum of money (as mentioned in the demand draft/banker's cheque) is transferred from the customer's account to a designated account of the bank. The recipient can deposit the cheque in his/her account and the money is transferred. When these types of cheques are issued to a recipient account in the same city, then it is called a Banker's Cheque. In case the recipient account is in a different city, then it is called a Demand Draft.
- RTGS and NEFT: Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) and National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) are electronic payment systems that enable banks to transfer money from one account to another without using any physical modes. While they can be done by submitting physical forms in bank branches, the best way to do RTGS and NEFT is by using net banking. The best part is that the fund is transferred within 30 minutes of making a request to the bank. When the transfer amount is less than ₹2 Lakhs, then NEFT is used, and if the transfer amount is ₹2 Lakhs and above, then RTGS is used. Earlier, RTGS and NEFT services were available only during banking hours and during bank working days. But since Dec 2019, NEFT & RTGS services are available 24x7x365 as instructed by RBI.
While performing NEFT or RTGS, customers need to quote the IFSC Code or the Indian Financial System Code of the recipient’s bank branch. It is an 11 digit code that identifies the right branch where the bank account is located. Every bank branch in India has a unique IFSC Code. For example, the IFSC Code of Kotak Mahindra Bank Nariman Point is KKBK0000958. - IMPS: Immediate Payment Service(IMPS) enables a customer to transfer funds instantly to any account within India using net banking or mobile banking. This service is available 24 X 7, throughout the year including bank holidays. The recipient account has to be in a bank that participates in IMPS. As of 2018, 53 commercial banks and 101 rural, district, urban, and cooperative banks participate in IMPS. A customer can transfer up to ₹2 Lakhs per transaction using IMPS.
International Transfers
Customers may need to transfer money to bank accounts located outside a country. These are called international transfers and can be done in two ways - Foreign Currency Demand Drafts and Remittances. Since these transactions are done in foreign currencies, an exchange rate is involved in this case. Each bank issues its own exchange rate every day which is based on the applicable Inter-Bank Rate of that day.
- Foreign Currency Demand Drafts: Commonly referred to as FCDDs, these are the foreign currency counterparts of demand drafts mentioned above. They are issued in a foreign currency such as the US Dollar or Euro and are payable to a customer's account located in a different country.
- Remittance: This is similar to RTGS or NEFT, however, the recipient is located in a foreign country. The transfer is done using SWIFT - Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication. SWIFT transactions can be completed online or through a bank branch. Each branch of the bank has a SWIFT code which needs to be mentioned to route the money to the right branch of the bank. The SWIFT code of the recipient’s bank branch has to be mentioned during each transfer for routing the money to the right account.
Since these are foreign transactions, the bank might ask for documents related to transactions such as the purpose of transferring money, passport, and others. For example, Kotak Mahindra Bank requests its customers to sign a form (A2) in case the cumulative amount remitted through an account in a financial year exceeds USD 25,000.
Each bank has a limit to the maximum amount of money that can be transferred during each transaction. Sometimes, banks can have a limit to the minimum amount that can be remitted as well. For example, Kotak Mahindra Bank has a robust remittance system called Click2Remit where the minimum amount per transaction is USD 100 and the maximum amount is capped at USD 5000 per transaction, USD 15,000 per week, and USD 20,000 per month (subject to 12 transactions per month).
Cheque Truncation System (CTS)
Satish wondered how money gets transferred from one account to another so easily in case a cheque is issued. He knew that the cheque has to go through RBI, but did not understand how does the cheque travel from the ATM (when a cheque is dropped at a dropbox in the ATM) to the bank and then to RBI and then to the recipient’s bank within a few hours of depositing a cheque in an ATM?
The bank representative smiled at this question and informed Satish about the Cheque Truncation System or CTS.
CTS is a cheque clearing system used by RBI for quicker clearance of cheques. It is a system through which the flow of the physical cheque has been discontinued and the electronic image of the cheque along with vital data is transferred instead. This system has brought elegance to the whole cheque processing activity. It has also benefited the banking system in terms of time and cost savings and cost-effectiveness. This process was implemented on 1st April 2013.
All CTS cheques hold a watermark with a ‘CTS-INDIA’ mentioned which is visible against any light source. A pantograph with a wavelike design and a hidden and embedded word ‘VOID’ is also visible in the photocopies of a CTS cheque. In general, ‘CTS 2010’ is printed on all cheques near the perforation which is visible to the naked eye.
Benefits of the Cheque Truncation System:
- CTS is an advanced and secured system.
- It enables quicker clearance of cheques.
- The CTS system has saved time, money, and manpower by doing away with the need for physical movement of cheques between banks and RBI.
- It has reduced the probability of misplacement of cheques due to physical transfer.
- It has reduced the possibility of fraud related to the clearance of cheques.
Begin your finance journey today with 'A2Z Of Finance: Finance Beginner Course.' Enroll now to master banking awareness and more
Keeping A Bank Account Secure
Having learned all the above concepts, Satish also wanted to know how to keep his account secured. Just the week before, his colleague encountered a pickpocket and within minutes, substantial money was withdrawn using his ATM card. Satish did not want to face such a situation and hence wanted to know what he can do to ensure his account is safe.
The bank representative told him that security is of primary importance when it comes to bank accounts. It is essential to follow certain precautions to ensure that the customer’s money is safe. Below are a few precautionary steps that customers should follow:
- Keeping the PIN and passwords secret: This is one of the primary ways to keep an account secured. Passwords and PINs should be kept secret and never shared with anyone over email, SMS, or even verbally.
- Using a strong password: It is also important to avoid using passwords such as the customer’s own date of birth, anniversary, kid’s date of birth, etc. which are obvious to guess. Most banks require customers to use one capital letter and one special character within the password to increase the strength of the password.
- Changing passwords regularly: Another essential activity is to change passwords once every few months. This reduces the chances of hacking.
- Never sharing account information over phone or email: No bank calls or emails customers asking for confidential account details such as PINs or passwords. In case customers receive such emails or phone calls, they should become careful that someone is trying to hack the account and inform the bank immediately. Most importantly, such emails or calls should never be entertained.
- Checking the account activity regularly: Customers need to keep a track of their account so that any abnormality can be easily identified. Logging in to online banking to view recent transactions or examining the monthly statement always helps.
- Not using public networks: Customers are strongly advised not to open their net banking account using public networks. Public networks are usually unsecured and they increase the chances of hacking an account manifold.
- Using good anti-virus protection software, firewalls, and spyware blockers: It is essential to invest in good computer protection tools to reduce the vulnerability of cyber attacks and fraud attempts.
- Reporting lost cards immediately to the bank: It is most essential to report lost cards or any fraudulent activity immediately to the bank. This will help the bank to block the card immediately and prevent any transaction in the card.
- Being aware of the surroundings in ATMs: A lot of fraud happens in ATMs. It is essential to keep an eye on the people around them while customers use ATMs. If it is a single machine ATM, ideally, no one else should be inside the ATM apart from the customer himself, not even the security guard.
- Taking receipts in ATMs: People often get impatient after withdrawing the money and walk off without collecting the receipt. Sometimes, they toss the receipt in the trashcan of the ATM itself. It is essential to collect the ATM receipt and keep it safe for a day or two. The information on the receipt can be used to fraudulently access an account. Keeping the receipt will also help customers in case some issues arise regarding the debit of the cash amount.
- Shredding documents and old cheques: Any document containing customer’s personal information should always be shredded. The information can be used to access the accounts. The same goes for old cheque books.
- By not leaving blank spaces in cheques: Customers are strongly advised to not keep any blank spaces in cheques. Any blank spaces should be struck off.
Satish learned quite a lot from this visit to the bank. He signed his online banking forms and was excited to try out the portal.
Safety Rules And Guidelines
As mentioned previously, Satish's friend had lost his wallet and within a few minutes, a substantial sum of money was withdrawn from his account. So Satish was very concerned about how to keep his account secured and make sure he doesn't have to face such a situation. After hearing about certain ways to keep his account safe from the bank representative in his previous visit to the bank, he wanted to know more. He researched online and this is what he learned.
Security guidelines to follow regarding ATM card and PIN
A lot of fraud takes place by misusing the ATM card and the PIN because it is an easy way to take out cash. Hence, keeping them safe is most essential. Customers should take the following safety measures:
- Observe the surroundings before using an ATM. If the machine is obstructed or the ATM area is poorly lit, customers should avoid using that ATM.
- No one else should be there in the ATM apart from the customer himself/herself, not even the security guard. The customer should not use an ATM in the presence of anyone else.
- Always shield the screen or keyboard while using the ATM so that the PIN and other details are not visible to anyone else, even to the CCTV camera.
- Keep the card, cash, and receipt safely immediately after using the ATM. Customers are advised to take a few seconds to do this before leaving the ATM vestibule.
- Always keep the card in a safe place and neatly to avoid damage or theft.
- Never write down the PIN anywhere. The PIN should be memorized.
- While choosing a PIN, avoid numbers that can be easily guessed such as the customer's own birthday, anniversary, spouse's birthday, telephone number, etc.
- Always change the PIN issued by the bank.
- Under any circumstance, if the customer feels that the PIN has been compromised, the customer should immediately visit an ATM and change the PIN.
- If the customer feels that the card security has been compromised at any moment, the customer should immediately call the bank, block the card, and request the issuance of a fresh one.
- Always collect ATM receipts for cash withdrawals and check the same against the transaction of the account. This can be done easily using net banking.
- The customer should always register their phone numbers with the bank and sign up for SMS alerts to receive SMS about transactions. This will help them identify any wrongful transactions immediately.
Using ATM cards internationally
Customers often use ATM cards at international ATMs. However, this makes their card susceptible to fraud in a foreign land. This is why many banks do not allow international usage. Customers should take extra caution while using their ATM card abroad and never use it if they feel vulnerable.
Fictitious Emails, SMS And Phone Calls
The convenience of digital banking has come with its own vices. Customers often receive emails where someone wants to leave them their inheritance of millions of dollars and are asked to share their bank account details to receive the money. While reading this, Satish remembered an email he received a few days back about someone in distress in Europe asking for some financial assistance from him.
These emails are called Fictitious Emails. Unfortunately, they are not restricted to emails only. Such requests are also sent via SMS. Sometimes, customers receive phone calls where people claim to provide them some gifts and ask for confidential details such as ATM PIN, CVV number, and the expiry date of cards over the phone. It is important to remember that banks never communicate with customers asking for confidential data.
In banking terms, the process of obtaining confidential banking information through any channel is known as Phishing. All banks send communications to customers at regular intervals requesting not to reply to phishing emails, SMS, and phone calls.
Ways to identify a fictitious email, SMS or Phone Call
Even the smartest customer can get conned at the wrong time. Here are a few things that can help customers understand that communication is fictitious:
- Any communication requesting personal information such as password, PIN, debit/credit card details, date of birth, etc. will be fictitious. Banks never ask for such confidential data except for the date of birth.
- Any email containing links to download unknown attachments can be fictitious. If the customer has used net banking on the computer through which he clicks on such links or downloads unknown files, the net banking password can be hacked.
- Any requests by institutions customers don't have a relationship with should be kept under suspicion. Apart from promotional emails/SMS, any institution where customers don't have an account will not ask for customer details.
- Any phone call from people claiming to be calling from banks and asking for personal details.
- Any communication mentioning that the customer has won a lottery has inherited money from an unknown source, someone is in distress, and anything which is suspicious.
What should a customer do if such communication is received?
First and foremost, the customer should not panic. A lot of mistakes happen because of panicking. Often people call over the phone and talk in a hurried manner so that the customer panics and gives out confidential information. Bank representatives have a protocol to follow. They will never speak in a hurried manner.
If the communication is an email or SMS, the same has to be deleted immediately. In case of an email, customers need to ensure that the same has been deleted from their trash folder as well.
In case a customer mistakenly replies to such communication, he/she should inform the bank immediately to help them take precautionary measures.
Forged Notes
Recently a few weeks ago, an incident took place with Satish while he visited the bank to deposit cash. While making the deposit, the teller of the bank found out that one of his ₹500 notes was fake, and he immediately stamped the 500 rupees note as fake and impounded it. Watching this in front of his eyes, Satish was devasted, and he promised not to fall for these fake notes again. He immediately went home and learned useful insights.
What are ‘Forged notes’?
A forged note, also known as a fake note or a counterfeit note is a currency note which has not been legally issued. A forged note does not have one or more features of an authentic note. It can be identified by seeing, touching, and tilting the note.
Each denomination of currency issued by the RBI has certain identifiable features, which are published by RBI. These include features such as a watermark, security thread, fluorescence, etc. A forged note will not have one or more of these features.
Measures were taken by RBI to address the problem of forged notes
RBI takes regular measures to counter the problem of forged notes. These include:
- Periodically improving the security features of notes so that forging becomes difficult.
- Ensuring that banks have a robust system in place to identify and detect forged notes.
- Raising public awareness on the issue.
- Improving coordination between banks and legal authorities.
What should a person do if he/she has unknowingly come in possession of a forged note?
Everyone should know the features of a legal note and assess the authenticity of notes in his/her possession. In case a forged note is submitted to the bank, the bank will impound the same and issue an acknowledgment to the customer. The bank thereafter sends the counterfeit note to local police authorities for further action.
In case the person knows of anyone who is involved in such activities, the person should immediately contact any of the law enforcement agencies as per Section 39 of the Criminal Procedure Code.
Ponzi Schemes
In the journey towards safeguarding oneself from fraud, it is essential to know about Ponzi Schemes. A Ponzi Scheme is a type of investment scheme where people are lured to invest their money in certain avenues with a promise to get a return at a later date. In most cases, the rate of return is very high to make a person greedy. Such Ponzi schemes maintain the illusion of running a business for a long time.
There are innumerable examples of such schemes across the world dating back to as early as the 1860s. The number of Ponzi schemes is surprisingly high even today. In fact, in 2017, 63 companies were identified as Ponzi schemes across the world. Some of the most famous Ponzi schemes in India include Sahara, Saradha, and Rose Valley where many people have lost their life savings.
How to protect oneself from Ponzi schemes?
It is easy to get lured by promises of high returns, however, it is essential to be aware. One mistake can lead to the loss of a lifetime.
Here are a few things customers can do to protect themselves from Ponzi schemes:
- Choose wisely: An investment manager is as valuable as a lawyer or an accountant and hence has to be chosen wisely. The same goes for investment avenues. It is always advised to invest money in reputed companies that are monitored by regulatory agencies such as the RBI and SEBI.
- Use common sense: A high return can look lucrative, but is it feasible? When most banks are giving a return of around 8%, is it possible for an organization to pay a return of 15%? Using a little bit of common sense can go a long way.
- Ask for proofs: It is easy to claim but difficult to produce reports. Customers need to check past performance and see proof of the promised returns. Such proofs should always be printed in letterheads.
- Ask questions: It is their own money and hence, customers have a right to know. They should always ask questions and know where their money is being invested.
Keeping the hard-earned money secured is not a difficult task. By being vigilant and by using common sense, it is possible to not fall prey to any fraudulent schemes.
Borrowing Money
After working for 6 months, Satish wanted to buy a car. He had saved some money for the down payment. He now wanted to avail of a car loan. However, before approaching a bank, he decided to learn about loans and understand how they work.
What is a Bank Loan?
A bank loan is a fund advanced by the bank to its customers. In return, customers pay a certain sum of money to the bank as interest on the money. Banks can loan the money for a specific purpose such as a car loan to buy a car or they can provide funding for a general-purpose such as a personal loan that can be used for any purpose.
Every loan is provided for a specific time period within which the repayment has to be made. Customers pay back the principal and interest amount in installments which are known as Equated Monthly Installments or EMIs. Each EMI consists of a principal and an interest amount.
Satish wanted to avail of a loan of ₹ 500,000 to buy the car. He found that Kotak Mahindra Bank offers car loans at an interest of 8.5% per annum as of March 2019. He calculated that the EMI for 5 years will be ₹ 10,258.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Loans
It will be wise to have a look at the advantages and disadvantages of loans:
Advantages of Bank Loans
Cost-Effective: Among all the financing options, bank loans have the lowest interest rate. Instead of taking loans, customers can meet their financing requirements using credit cards or overdrafts from banks. However, the interest rate on them will be much higher than that in loans.
For example, a person looking for some funds for personal use can either opt to use his/her credit card or take a personal loan from a bank. However, he/she will have to pay an interest of around 2.5%-3.00% per month in case of a credit card as against a flat 12% (March 2021) per year interest on a personal loan taken from Kotak Mahindra Bank. Hence, the personal loan will work out to be more cost-effective.
Flexibility: Since at the time of taking a loan, the customer is aware of the EMI amount and the time period for which the repayment will continue, customers have the independence to plan their finances. Moreover, in the case of loans, the EMI amount is automatically debited from the savings account of the customer removing any hassle of manual payment.
Retaining Earnings: When it comes to running a business, loans are the best way to finance them. Since the company pays an EMI, profits can be retained by the shareholders.
Tax benefits: Certain loans such as home loans provide tax benefits to the borrower. While filing income taxes, customers can claim tax benefits on the interest paid on the home loan for that financial year.
Disadvantages of Bank Loans
Repayment Burden: Loans have to be repaid over several years. In some cases, this may be more than a decade as well. For example, typically a home loan is taken for 15 to 20 years and the EMI has to be repaid over the next 20 years. This might put a financial burden on the borrower.
Strict Requirements: Banks have very strict requirements regarding documentation before providing any kind of loans. Banks take a risk by giving out a part of their fund to a customer. Hence, it is imperative for them to conduct the necessary background check and be sufficiently satisfied regarding the repayment ability of the customer. For people who don’t have their documentation organized, this process might look tedious, even worrisome.
Types of Bank Loans
In India, banks provide a wide variety of loans which can be for personal use or business use. The most common types of loans include:
- Home loans, which can be further subdivided into:
✔ Home Purchase Loan
✔ Land Purchase Loan
✔ Home Construction Loan
✔ Home Extension Loan
✔ Home Renovation Loan
✔ Stamp Duty Loan
✔ NRI Home Loans
✔ Loan Against Property
- Personal loans
- Business loans
- Education loans
- Gold loans
- Car loans
- Two-wheeler loans
- Loan against securities
- Loan against the insurance policy
- Loan against PPF
- And others.
Each bank has the liberty to design its own loan product, which has to be done following guidelines laid down by RBI. For example, Kotak Mahindra Bank’s loan products include home loans, car loans, personal loans, education loans, gold loans, loans against securities, and loans against property.
Banks can also decide the interest rate that they will charge on respective loans. However, RBI provides guidance for fixing the interest rates by publishing a guidance rate known as the ‘Base Rate’.
Let us now look at some of the most popular loan products offered by banks:
Home Loan
Home loans are loans where the bank finances up to a certain amount of the cost of buying a house. These are extremely beneficial for purchasing a property which might be too expensive to be paid as a lump sum by an individual customer. Home Loans have made housing affordable for customers. Banks fund up to a certain percentage of the cost of the property. This percentage of funding varies from one bank to another. Kotak Mahindra Bank finances 75% to 80% of the cost of the property. Since the principal amount is quite hefty, home loans are provided for a longer period, between 15 to 20 years. The property remains mortgaged with the bank till the time the full payment is made to the bank.
Car Loan
Having a car is no more a luxury today. Car loans make purchasing a car easier for customers where the bank funds a certain portion of the cost of the car. Customers can use a car loan to buy a new as well as a used car. In the case of car loans, the car remains mortgaged with the bank till the time the full payment is made to the bank.
Personal loan
These are loans provided by banks to meet miscellaneous requirements such as going on a vacation, wedding in the family, purchasing household electronic items, meeting emergencies in the family, and others. This is an unsecured loan that is granted solely on the repayment power of the borrower.
Education Loan
Higher education is quite expensive nowadays. However, education loans make it easier to fund them. Education loans are deferred loans that fund the years of education of a student, and the repayment starts after the student has secured a job. These loans are designed to help meritorious students achieve their dreams. Although education loans are primarily unsecured, banks might require some kind of mortgage such as an insurance policy.
Gold Loan
Traditionally, Indians value gold, and usually each household owns a decent amount of the same. However, in most cases, gold lies idle in a bank locker or at home. Gold loans are a way to make the idle gold work for customers when they are in need of funds. In gold loans, the gold is mortgaged at the bank and a certain amount is given out as funding. The customer pays EMI in return and once the loan is closed, the gold is given back to the customer.
Loan against Properties
When customers are in need of funds, banks can provide loans by mortgaging properties held by customers. As in all other loans, this is also provided based on the repayment capacity of the customer. Once the loan is fully repaid, the property papers are returned back to the customer.
Credit Cards
What is a Credit Card?
A credit card allows someone to borrow money from a bank for purchasing products/services. The bank approves a line of credit to its customers through a credit card which is the amount that the customer can borrow from the bank. The payment can be returned to the bank over a period of time. Through a credit card, the bank approves a credit limit to each customer based on factors such as the credit score, repayment capacity, previous history with the bank, etc. The customer is at liberty to use the credit card up to the amount mentioned in the credit limit.
A statement is issued for a credit card every month which contains the total amount, the payment date, and a minimum amount. In case a customer fails to pay the total amount, the bank levies interest on the outstanding amount. The interest rate varies from one bank to another and can be different for different credit cards issued by the same bank.
Every customer has a credit score which reflects the financial health of the customer. Timely payment of credit card bills helps to build a positive credit score, however, missing out payments can affect it negatively.
Usually, each bank has a variety of credit card products that differ from each other in terms of features. Some might provide better reward points on shopping while others may provide airline mileage. For example, Kotak Mahindra Bank offers 20 different kinds of credit cards to its customers. Customers should compare the features of different cards and choose the one that suits their needs.
Terminology related to Credit Cards
Credit Limit: Credit limit refers to the maximum amount approved by the bank for a certain credit card. A customer can use the credit card up to this amount only. For example, if the credit limit of a card is ₹ 100,000, a customer can use the card up to ₹ 100,000 only.
Total Amount Due: This refers to the total amount owed by the customer to the bank. A customer can choose to pay the full amount or a part of the same to the bank at any point in time. The bank levies interest on the portion of the total amount which is not paid back to the bank on the payment due date.
Minimum Amount Due: This is the amount that a customer has to compulsorily pay to the bank on the due date. Usually, the minimum amount is 5% of the total amount due. While the customer may or may not pay the entire amount due to the bank, the minimum amount has to be paid back. This is not an optional amount.
Payment Due Date: This refers to the last date by which the payment has to be made to the bank for a given statement.
How to use a credit card?
Upon approving an application, the bank provides a physical card and a PIN to a customer. The card and the PIN are sent to the customer through two different couriers to remove the chances of any kind of fraud by the courier personnel. A customer is allotted a credit limit on the card which can be used by swiping the card physically to make purchases or using the card online. Each card also has a cash limit, which is a portion of the total credit limit. This refers to the amount of cash that the customer can withdraw from any ATM using the credit card. The customer has to use the PIN for using the card in any of the above scenarios. The PIN negates the chances of misuse of the card, should it fall in the wrong hands.

What is a credit score?
A credit score is a number associated with an individual that relates to his/her debt repayment habits. It helps banks and lenders to decide whether they will approve a loan or advance or a credit card in his/her favor.
This is done worldwide in almost every country for its citizens. In India, the agency which calculates and publishes the credit score is called Credit Information Bureau (India) Limited or commonly CIBIL. It publishes a 3 digit CIBIL Score for individuals which is the credit history of an individual. It includes the credit repayment history of the individual across all loans and across all institutions. The score is calculated considering various factors such as the number and types of loan accounts held by someone, payment history, number of outstanding loans, and others.
CIBIL generates a CIBIL report for individuals which contains a comprehensive overview of all loans taken by a person. It also contains the loans for which an individual has signed as a guarantor.
While granting loans, banks take the CIBIL score into serious consideration.

Advantages of maintaining a good CIBIL score
CIBIL score plays an important role in a person’s financial journey. Some of its advantages include:
- Ease of getting approvals on loans by financial institutions
- Quicker approval of loans by financial institutions
- Lower interest rates on loans
- Ease of obtaining credit cards
- Lower interest rates on credit cards
- Ease of renting or leasing houses
Importance Of Maintaining A Good CIBIL Score
The CIBIL score is very important for availing credit from any financial institution. A CIBIL score is the first impression of the lending organization about a borrower.
Maintaining a good CIBIL score is of tremendous importance. Below are the aspects which are influenced by CIBIL scores:
Credit Approvals
If there is one thing that matters the most while banks take the decision whether to grant a loan to an individual, it is the CIBIL score. A bad CIBIL score reduces the chances of getting financing of any kind. On the other hand, a good CIBIL score may make things a cakewalk.
Interest Rates
CIBIL score is a determiner of the interest rate at which the bank will offer a fund to an individual. The better the credit history, the better will be the interest rate.
Other Activities
Organizations outside the financial industry have now started using the CIBIL Score as well. A good CIBIL score might help someone get a better mobile plan or a discount on insurance premiums.
Problem Of Excess Debt
Global Debt reaches a whopping $226 Trillion as per the IMF report of 2020. The debt problem is bad worldwide. Since funds are so easily available nowadays, people get into a humongous burden of debt even before they realize it. Then paying it back gets next to impossible. Sometimes people take one debt to pay off another such as they take a personal loan to pay off a credit card due. Then once the credit card limit is free, they start spending on the credit card again and land up with a personal loan and a high credit card due to pay off. More and more people across the world are falling prey to this. This is called the 'Debt Trap.'
The most common reasons for going into an unreasonable amount of debt include:
- Irresponsible Spending: Spending money irresponsibly is the numero uno reason for falling into a debt trap. Credit cards give a false impression of possession of money to people and it is easy to overspend.
- Wrong Habits: People who have a habit of gambling can accumulate a lot of debt over a short period of time.
- Poor Savings: People may not pay much importance to savings and may not have a sufficient sum of money to meet emergencies. In such cases, they might have to rely on loans to meet sudden expenses.
- Medical Emergencies: Medical emergencies can arise anytime anywhere and can affect anyone. Treatments are costly and might leave a family with a burden of debt.
- Loss of Income: During an economic downturn, one might have to rely on loans to meet the basic expenses. With a reduced income, this can lead to the accumulation of debt.
Strategies To Avoid Excess Debt
So, to tackle this colossal debt crisis, here are a few strategies to control excess debt:
- Living within means: As mentioned earlier, the easy availability of funding gives people the false impression that they have money, although they don’t. It is advisable to understand what one can afford and make purchasing decisions accordingly. Every household has some necessary items that are required every month such as groceries and utilities and some luxury items that are optional such as vacations. Making prudent decisions considering one’s spending power is the best way to avoid the accumulation of debt.
- Paying off the total amount in a credit card: Most people who are in the debt trap have high unpaid credit card bills. Full payment of credit cards is absolutely essential to control one’s debt situation.
- Building an emergency savings fund: Everyone should keep aside a certain sum of money every month for emergencies only. Emergencies always come unannounced. Having a designated fund for emergencies will help someone meet the expenses and avoid taking any loans during that phase.
- Investing in insurance: Medical treatment is becoming more and more expensive. Having a good medical policy is the best way to meet treatment costs. This also negates the requirement to take debt for such purposes. It is also essential for the main earning member of the family to have a good insurance policy so that the family does not fall in trouble in case of the death or disability of the earning member.
What are the various strategies that can be employed to control Existing Debt?
Thousands across the world are already burdened with huge amounts of debt. Here are some strategies to manage already high amounts of debt:
- Avoid further accumulation: The first thing to do is to stop accumulating more debt. The person facing the situation needs to control spending to stop piling up the load.
- Take stock of the situation: The next step is to understand the situation. This will include making a complete list of all the amounts that the person owes to different institutions.
- Work out a payment plan: The final step is to make a payment plan. The person needs to understand how much he/she can afford to pay per month and then make a plan to pay out the debt one by one. The ones with the highest interest rates should be paid out first.
A little bit of discipline is all it takes to clear out a debt situation. Although the task might look massive in the beginning, however, a few months of discipline will make the entire situation quite manageable.
Managing Money
An age-old saying goes “A penny saved is a penny earned”.
Managing one’s finances is as important as earning money. While Satish has been saving up some amount every month from his salary, he never followed a kind of discipline. However, he has seen some of his colleagues maintaining excel sheets of their bank account transactions and tracking the same meticulously.
One day, while having lunch, he asked his colleague why he tracked his bank account manually. This started off a conversation where Satish got to know a lot of valuable things.
How to manage finances?
Managing finances is extremely important. While managing one’s income such as salary may not be in someone’s hand, managing what people already have with them is easier. Managing finances gives someone the leverage to increase income and cash flow to a considerable extent. A few wise decisions such as investment in the right avenues, purchasing insurance policies, creating an emergency fund can greatly affect financial security during a person’s lifetime and even beyond.
Ensuring better control of funds in bank accounts: Having better control over funds is imperative to avoid untoward situations. Without proper control and tracking, people often lose track of their money. Then they have to face situations like insufficient funds while withdrawing money from an ATM, unavailability of the fund in case of emergencies, etc.
Once Satish learned about this, he realized that it is his own money and no one else can look after it the way he can. His colleague told him the following methods to have better control over his funds:
Keeping a track of the fund in the bank: It is a great practice to keep a manual ledger balance of the bank account. In case, someone is unable to do so, he/she should at least log into the account at regular intervals and reconcile the transactions in the account. This tracking will also help in identifying any error or fraud immediately which will enable the bank to take appropriate action.
Signing up for multiple channels of banking: A great way to have better control over the funds is to sign up for all the services the bank has to offer such as email statements, SMS alerts, net banking, and mobile banking. This way, a customer can stay informed through multiple channels about any debit or credit in the account.
Keeping in touch with the bank: It is essential to keep in touch with the bank for obtaining help when needed. Those who can visit branches may make acquaintances with someone at the branch. Those who cannot remain in touch by using Phone Banking. Banks assign relationship managers to customers. These relationship managers are qualified to finance professionals entrusted with the job of taking care of all the customer’s needs. They visit a customer’s office or home to remove the hassle of visiting the bank for the customer. These relationship managers are trained on all kinds of banking procedures as well as handling investments. They are of great help to customers.
Nomination Facility In Bank Accounts
One of the foremost responsibilities of the earning member of a family is to make provisions so that the family can have easy access to all funds in his absence. All banks extend the nomination facility to its customers to make this process smoother. Through this facility, an account holder can nominate anybody of his choice to receive the fund in case of his/her death. This nomination facility is available to all types of accounts including joint accounts and safe deposit lockers. The name of the nominee is printed in bank documents for easy understanding.
The nominee can be any individual, even minors. In case the nominee is a minor, an appointee has to be fixed who may or may not be the guardian of the minor. In case of a fixed deposit, the original nomination continues even when the fixed deposit auto-renews.
A customer can change a nominee any number of times in a particular bank holding. The rights of nominees come in force only upon the death of the account holder.
The process of designating a nominee is extremely simple and can be done by simply signing a form (Form DA1). Similarly, the cancellation of a nominee is also extremely easy and can be done by signing (Form DA2).
Importance of designating a nominee
In India, the awareness regarding the nomination facility is quite low. In fact, RBI reports that more than ₹ 1000 crore of unclaimed money is lying across different banks due to the absence of a nomination facility. When there is no nomination in an account and a dispute arises after the death of a customer, the money lying in the account will become disputed and will not be handed over by the bank to anybody, thus lying idle as unclaimed money. Such disputes can be fixed through a legal process only which can be time-consuming.
It is impossible for anyone to understand what the situation will be upon his/her death. Having nomination in any account smoothens the process of transfer of funds to any person favored by the account holder to receive the money.
Rights of a nominee over an asset
It is commonly assumed that nomination gives someone the right to an asset. Be it a bank account, insurance policy proceeds, or a property, people think that the person who holds the nomination will get the rights.
However, in reality, although the nomination holder receives the asset of a deceased, the rightful owner of the asset is the legal heir(s) of the deceased. The nomination holder is merely the receiver and the holder of the assets of the deceased till he/she is legally bound to transfer the same to the legal heir (s). This has been a center of massive discussion over several years which was finally brought to an end in 2006 by the Hon Supreme Court of India over a dispute regarding a flat in a cooperative housing society in Kolkata. In its verdict, the Court said that the flat would be transferred to the nominee but the legal heirs hold the right to ownership of the flat.
Following this, RBI has clarified that the same applies in the case of deposits held by the bank. The nominee shall receive the proceeds only “as a trustee of the legal heirs of the deceased”. Hence, in case of bank deposits, all proceeds are duly transferred to the nominee. A bank’s responsibility ends with such a transfer. Banks will not be involved in further legal proceedings.
It is essential to note that this applies to bank deposits only. The scenario can be different for different assets such as mutual funds or property.
Procedure For Making A Claim
The procedure for making a claim differs for different kinds of accounts held with the bank.
Savings/Current Account/Fixed Deposit
In case of the death of a customer where the account had a single holder, the proceeds are paid to the nominee. In such a case, the nominee has to provide proof of death of the holder and the nominee’s identity proof. In the case of the first holder expires in a joint account, the proceeds are paid to the second account holder. The bank will take proof of the death of the first holder to process such a claim. In case the second account holder expires, the first holder can approach the bank to remove the name of the second account holder by providing proof of death. In case of the death of all holders in a joint account, the balance is paid to the nominee. In case there is no nomination in the account, the proceeds are issued in favor of the legal heir. In this case, the proof of the legal inheritance will have to be submitted to the bank.
Safe deposit lockers
In the case of the death of one of the joint holders in a locker, the other joint holder and the nominee will be jointly allowed to access the locker and remove the content. In case of the death of all holders, the nominee is allowed to access the locker. The nominee will be required to provide his/her proof of identity as well as proof of the death of the account holder. However, in case there is no nomination facility, the legal heir can access the locker and remove the content. In this case, the bank will verify the proof of inheritance. In all cases, the bank will make an inventory list of items inside the locker and record the same.
After learning all the things related to nominations in bank accounts, the first thing Satish did was to visit his branch and sign a nomination form for his savings account and fixed deposit. He felt peaceful that in his absence, his mother would be able to use his money to run the family.
Digital Money
The world has moved to the digital space, so has banking. The practice of carrying around hefty amounts of cash is history now, thanks to Digital Money.
An overview of Digital Money
Digital Money is any money that is exchanged by the use of technology such as mobile phones and computers. Credit cards, debit cards, and online cryptocurrencies are examples of digital money. In some cases, digital money can also be transferred into physical cash, withdrawing cash from an ATM is a classic example of the same.
The concept of digital money evolved in the early 1990s when the internet started becoming popular. Several digital cash companies were formed as early as 1990, the most famous among them being DigiCash. However, most of these initiatives failed due to inappropriate integration with the internet.
Digital money has come a long way since. Today, people think twice before using cash but hardly hesitate to use digital money. From purchasing retail products to making payments to someone located across the globe, anything is possible using digital money.
Importance of digital money
Literally speaking, digital money is basically a certain number on a screen. It can be transferred instantly and does not need currency to be physically moved from one place to another. It has reduced the time of transactions, especially when the payer and the payee are located thousands of miles away. There can be a fee associated with storing and transferring digital money, however, the same is justified considering the convenience factor involved with it.
Digital money is stored as data and hence is harder to lose. Although data is vulnerable to attack by hackers, financial institutions across the world undertake measures to protect these data.
Most importantly, digital money has opened up a plethora of opportunities worldwide. It can be used for purchasing products available anywhere in the world. As more and more organizations embrace digitization, the usage of digital money is becoming a matter of habit worldwide.
To sum up, digital money has three basic benefits:
- Convenience: They have negated the requirement to carry cash around. Payments can be made anytime to anybody located anywhere. People don’t even have to be present physically to pay or receive money.
- Easily traceable: All data is stored in digital form makes it easier to access. Every little transaction is recorded and hence easily traceable. This removes any kind of ambiguity regarding the tracking of transactions.
- Reduced risk: Since data is more difficult to tamper with than stealing hard cash, digital money has brought a sense of security to the entire financial system.
Forms Of Digital Money
The opportunities regarding digital money are endless. Innumerable products are available world-wide incorporating different kinds of digital money.
Some of the most popular forms of digital money include:
- Debit Card: One of the most popular forms of digital money is a debit card. It is a plastic card which is an alternative to cash. These cards are issued to access someone’s savings/current account digitally.
- Credit Card: A credit card is a plastic card that allows a person to borrow money against a line of credit. This line of credit is known as a credit card limit. A credit card can be used for making basic transactions. All transactions reflect on a bill commonly known as a credit card statement.
- Prepaid Card: These are plastic cards that are pre-loaded with a specific amount of money. The card can be used up to the balance loaded on the card. This card is not linked to any savings or current account. A common kind of prepaid card is a gift card which is often used to gift a sum of money to someone. Another useful prepaid card is a Forex Card which is issued in a foreign currency such as the US Dollar or British Pound. A Forex Card is loaded with a certain sum of money and can be used by people while they are visiting a foreign country. This has removed the requirement to carry physical foreign currency while traveling.
Prepaid cards are becoming popular day by day. Most banks offer a range of prepaid cards to its customers, each issued for a specific purpose. Kotak Mahindra Bank offers five different kinds of prepaid cards to its customers - Forex Card, Kotak Netc@rd, Kotak Best Compliments Card, FasTag, Kotak Connect.
Digital money issued through cards is popularly known as plastic money.
- Digital Currencies: These are online currencies that are exchanged over the internet, without being converted into cash. They are commonly known as Cryptocurrencies. It is a payment method that exists only in the electronic form. The acceptance of digital currency is yet quite low. However, they are gaining popularity worldwide.
- Digital-Payments: Digital payments or e-payments are options for making payments without having the need to physically move cash from one place to another. Banks across the world are continuously researching methods of online payment trying to make life convenient for its customers. The easiest form of online payment is RTGS, NEFT, IMPS and SWIFT discussed earlier in the book. Other popular forms of e-payments include ECS, e-payment of bills, mobile payment, and others.
- e-Wallets: e-Wallets or Digital Wallets as the name suggests are customer’s wallets held online. Customers fund these eWallets and use them for buying goods, paying bills, and a range of functions online.
Debit Cards
A debit card is a plastic card issued by a bank that is directly related to the customer’s bank account. The card can be used to make purchases either by swiping the same physically or using the same online. They eliminate the requirement to carry cash or physical cheques to make purchases. To eliminate the confusion of using multiple cards, banks usually issue a Debit cum ATM card to its customers so that customers can use the same card for making purchases as well as withdrawing money from ATM machines.
Since debit cards are linked to a bank account, they can be used only up to the amount lying as balance in the same account. Additionally, many debit cards have a daily limit for each transaction such as Kotak Mahindra Bank’s #PayShopMore Debit Card has an ATM withdrawal limit of ₹ 40,000 and a purchase limit of ₹ 200,000 per day. This is primarily fixed to secure the card against fraudulent usage.
Usually, each bank has a variety of debit cards and the kind of debit card offered depends on the type of account held with the bank. Kotak Mahindra Bank has 14 different kinds of debit cards for its customers.
Although the primary function of debit cards is to ease transactions, most banks offer innumerable facilities attached to debit cards to make the card propositions more attractive for the customers. Such facilities may include reward points, airline mileage, inbuilt insurance attached to the card, airport lounge access, personal accidental death coverage, and many more. For example, Kotak Mahindra Bank offers complimentary insurance of up to ₹ 55 Lakhs with its Platinum Debit Card, access to a large number of shopping deals with its #PayShopMore Debit Card, and Air Accident Insurance with its World Debit Card. It has several other such attractive propositions attached to each of its 14 types of debit cards.
While banks offer debit or credit cards, they are not the primary issuers of cards. The card is issued by an issuing organization which is a financial services corporation. VISA and Master Card are the two most famous financial services corporations across the world who issue cards. Rupay is an India based domestic card payment scheme launched by the National Payments Corporation of India. In India, most cards are issued by VISA, Master Card, and Rupay.
Digital Payments
Digital Payment is the exchange of money online by using computer networks, the internet, and digitally stored data. Commonly known as e-payment or online payment, this enables accepting and making payments online. It includes a transaction that results in the flow of money from one person to another. This exchange can take place between bank accounts, credit cards, or different payment solutions wallets such as PayTM, PayPal, etc.
The advent of online payment has made life easy for businesses as well as customers. Merchants can now accept payment online and customers can make payments online. The transfer happens over a secured encrypted connection. From purchasing products over e-commerce portals to paying monthly bills, online payment has made the payment system completely hassle-free.
Types of Digital Payments
Online payment or electronic payment refers to any kind of non-cash payment that does not involve a paper cheque. Credit cards, debit cards, automated cheque clearing are all methods of online payment.
Online payment can be used to make the following kinds of payments:
One Time Payment: Online shopping is no more an item of luxury, the convenience factor has made it a habit for many. When people shop online on e-commerce platforms such as Amazon and Flipkart, they make payments using digital payment options such as credit cards, net banking, or e-wallets. This payment is made on a case to case basis and hence referred to as One Time Payment.
Recurring Payment: There are some expenses that people have to incur every month. This includes monthly bills such as the electricity bill or a mobile bill. Earlier, people had to stand in line for hours to pay such bills. Now, they only need to click on a few buttons to complete payment. Customers can make monthly payments either by visiting the service provider’s website or by simply logging into net banking. Banks provide a range of options to customers to pay bills such as linking the bill to net banking for easy payment. This negates the requirement to fill in the details for payment every time customers make payments.
Automatic Payment: To avoid manual intervention every month for recurring payments and to remove chances of missing out on payments, customers can provide an auto-debit instruction to the bank to debit the bill amount from their bank account or their credit card on the bill due date. In such cases, the bill is paid without any manual intervention by the customer.
E-Wallets
e-Wallets are secured online wallets held by a customer for using funds online or offline. e-wallets need to be funded once and the balance in the same can be used to make transactions. For example, if an e-wallet is funded with ₹ 2000, it can be used to recharge a mobile phone for ₹500, buy groceries from a physical store for ₹1000 and purchase movie tickets online for ₹500. Once the balance of ₹2000 is used up, the same e-wallet can be funded again and the money can be used for further transactions.
e-wallets have become extremely popular in the last couple of years due to their ease of usage. Several providers offer e-wallets to customers worldwide. The most popular global e-wallet providers are Apple Pay, Samsung Pay, Amazon Pay, and Google Pay. They operate in India as well. India also has domestic e-wallet providers such as PayTM, MobiKwik, Jio Money, and others.
How to open and use an eWallet?
The process of opening and usage is a simple one which can be completed in just 3 steps:
Tapping an e-Wallet
One of the best features of e-wallets is ‘Tap’. e-wallets are specifically designed for usage on mobile devices and have loads of functionalities that work best on mobile phones. While making offline purchases, a person can simply open the barcode of the e-wallet and tap on a specific screen kept at the cashier’s desk and the transaction is completed immediately. There’s no need to exchange cash, swipe cards, or insert a PIN number. All people need to do is tap their mobile phones.
Functions that can be performed using e-Wallets
e-wallets can be used for a range of transactions. Some of the common ones include:
- Recharging mobile phones
- Paying mobile bills
- Paying utility bills such as electricity bills, water bills, broadband, etc.
- Paying school fees for children
- Booking train, bus, flight tickets
- Booking hotel rooms
- Paying insurance premiums
- Purchasing goods online
- Purchasing goods offline
Types of e-wallets
e-wallets are of three kinds:
- Closed e-wallets: Closed e-wallets can be used for making payments for the services provided by the wallet issuer. It cannot be used for making payments to any third party service provider. They do not have a cash withdrawal facility. The money credited into a closed e-wallet has to be used for making payment to the wallet issuer only. Uber Credits is a closed e-wallet that can be used for making payments for hiring cabs only.
- Semi-closed e-wallets: These are e-wallets that can be used for shopping and virtual fund transfer to another user in the same wallet network. These e-wallets can be used only for those merchants who are registered with the e-wallet provider. They do not permit cash withdrawal by the owner. Semi-closed e-wallets are very popular in India and are mostly used for online shopping. The best example of a semi-closed e-wallet is PayTM.
- Open e-wallets: Open e-wallets are similar to a prepaid card, but available online. They are issued by a bank with a pre-funded amount. The e-wallets can be used up to the pre-funded amount. They can also be used for cash withdrawal. They can be reloaded once the pre-funded amount is used up.
Unified Payments Interface
Any discussion on digital money is incomplete without a discussion of the Unified Payment Interface (UPI). UPI is a real-time payment system developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) for facilitating inter-bank transactions. This platform, regulated by the RBI allows instant transfer of funds between two bank accounts through a mobile platform. UPI was launched in 2016 and has been a significant step towards ensuring a cashless India.
UPI works round the clock 365 days a year and definitely scores high compared to RTGS or NEFT which works during certain operational hours and is restricted to bank working days only.
The UPI system has gained popularity over time. In 2020, UPI processed 18.87 billion transactions worth ₹31 lakh crore. The current year has already seen 34.18 billion transactions worth ₹63.2 lakh crore.
Process Flow of UPI
Transactions that can be done using the UPI system
While the UPI system allows a range of transactions, here are some of the common ones:
- Immediate fund transfer
- The transaction with multiple banks using a single mobile application
- Bill sharing
- Merchant payments
- Utility bill payments
- Donations
- Collection of money
How to use the UPI system?
Simplicity and convenience is the key while using any UPI system. The process of using the same is as follows:
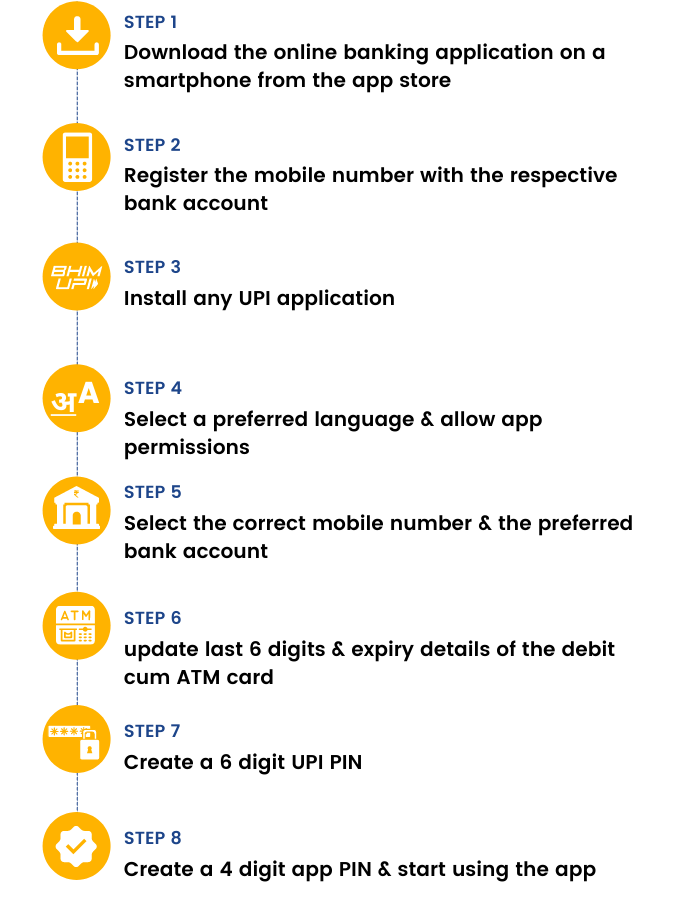
Benefits Of UPI System
The introduction of UPI has brought the following benefits to customers:
- 24 X 7 X 365 availability
- Transacting using a virtual ID without the requirement to share credentials repeatedly
- Accessing multiple bank accounts through a single app
- Authentication in a single click
- Availability of help when needed
Things to remember while using UPI
Users need to make sure that the mobile phone is locked using a secure PIN or fingerprint lock. Users need to ensure that the mobile number entered in the UPI system is correct.
The UPI PIN has to be entered every time a transaction is carried out. Hence, remembering the same is essential.
Being a Banker is an interesting profession full of learning opportunities. The industry is going through a revolution across the globe especially due to the most competitive digitization initiatives. New technology comes in every now and then making the previous ones irrelevant. Staying updated will lead the pathway to staying relevant.
Conclusion
Finally, this module has come to an end. Hope you learned quite a lot about the banking system in India, along with Satish. We have tried to cover all the basics related to banking. There are much more things to learn about banking and its services. A fun fact: Did you know that the banking and financial services sector has the highest weight of 39.47% in the Nifty 50 index? Yes, you heard it correct. It has got the highest weight among all other sectors. If you ask why so? Because of the importance of money flow in the economy. Learning does not end in our life. So, keep learning and read more such interesting modules at ELM School.


