Corporate Action
Corporate Action
What are Corporate Actions?
Corporate Actions implies action at the corporate level which has a significant impact on the stakeholders and the financial structure of the company. It is an event initiated by a public company that affects the securities (equity or debt) issued by the company.
Corporate actions are typically agreed upon by the company's board of directors and are authorized by its shareholders. It is undertaken mainly for either of the below mentioned reasons.
- Return profit to shareholders
- Influence the share price i.e., by enhancing liquidity of the stock in the secondary markets.
- Corporate Restructuring
Some of the popular examples of corporate actions include Right Issues, Bonus Issues, Dividends, Stock Splits, Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) and Spin-Offs.
Corporate Actions can be broadly divided into two categories.
- Mandatory
- Voluntary
Let us understand the difference between them.

Mandatory Corporate Action
It is an event initiated by the corporation by the board of directors that affects all shareholders. Participation of shareholders is mandatory for these corporate actions. Practically speaking, the shareholder is a passive beneficiary of these actions. Examples of such corporate actions are: Dividends, Stock Splits, Mergers, Bonus and Spin-Offs.
Voluntary Corporate Action
A voluntary corporate action is an action where the shareholders elect to participate in the action. The shareholder must submit his response to the company expressing his/her desire to be involved. Examples of such corporate actions are: Rights Issues, Buybacks, Early redemption of bonds issues, etc.
Note: There is another type of corporate action that is "Mandatory with choice," where shareholders are offered a choice to choose from. Shareholders may or may not submit their elections. If a shareholder does not submit an election, the default option will apply. An example of such corporate action includes cash/stock dividends, with the former being the default choice.
Actions such as the announcement of a dividend, bonus, rights issue and a buy back are viewed positively from the viewpoint of the shareholder. These are ways by which a company rewards its existing shareholders. On the other hand, a stock split done to increase liquidity and improve participation in a stock is viewed positively because as the price reduces, more and more shareholders are attracted and thus liquidity increases.
Corporate actions can be easily viewed on the website of the company or the corporate filings section of the NSE/BSE website. You can also find the same in the StockEdge app under the Daily updates section. Click here to view the upcoming corporate actions of various companies.
So, we have learned about Corporate actions and also their types. But what is the purpose of corporate actions? Let us discuss this in the next unit.
Purpose of Corporate Actions
What is the Purpose of a Corporate Action?
Corporate Actions are majorly undertaken by the company’s directors for the following purposes: -
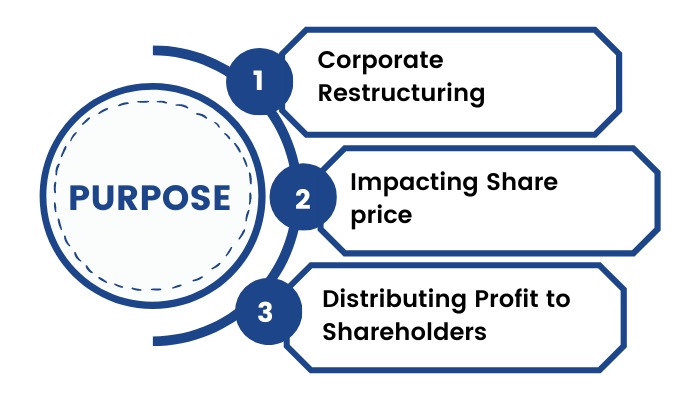
1.Corporate Restructuring
Corporate Restructuring can be thought of as a process that radically changes the contractual relationships existing between a company & its shareholders, employees, creditors & other stakeholders. It is done with a view to aid the long-term profitability of the company. Some of the common examples include Spinoffs, Mergers and Acquisitions, Debt Restructuring, etc.
The spin-off (creating a new company from the subsidiary or division of an existing parent company) of PayPal from its former parent E-Bay on July 15, 2015 is an example of corporate action undertaken for the purpose of Corporate Restructuring.
2.Impacting Share Price
The liquidity of the stock is greatly impacted if the stock price is extremely high/low. There is a general tradition amongst retail traders to shy away from high-priced stocks. On the other hand, if the price is too low, the stock might be perceived as a bad investment. Corporate actions like Stock Splits, Reverse Stock Split and Buybacks are used to influence the stock price.
For instance, In March 2020, Bajaj Steel Industries announced a stock split of 1 equity share of Face Value ₹10 each into 2 equity shares of ₹5 each.
3.Distributing Profit to Shareholders
The dividend distributed could be in the form of cash or stock dividends. In the case of a cash dividend, the company declares a dividend to be paid on each outstanding share. However, the bonus issue involves an issue of additional shares to shareholders instead of cash.
Note: We will discuss the concept of dividends in the next section.
In 2019, HCL Technologies issued bonus shares in a ratio of 1:1, i.e., existing shareholders of the company received an extra equity share for each share held by them.
What are dividends?
What is Dividend and Dividend Yield? How is it important for the investor?
Dividends
Dividends are the way by which a company returns back a part of its profits to shareholders. When a company earns a profit or surplus, that money can be put to two uses: it can either be re- invested in the business (called retained earnings) for future expansion projects or growth, or it can be paid to the shareholders as a dividend. Many companies retain a portion of their earnings and pay the remainder as a dividend. Dividends can be of three types.
- Interim dividend - usually paid quarterly
- Final Dividend - paid at the end of the financial year
- Special Dividend - paid under extraordinary circumstances when the company earns profit from an activity which is not in its scope of normal business. Say for example: An IT company earns profit from the sale of a land parcel.
Directors of a company have discretion as to how much of a dividend to declare or whether they should pay any dividend at all.
There are a few important terms that are important for an investor to know with respect to dividends.
- Dividend Declared = Face Value of the share X % Dividend Declared
- Dividend Yield = Annualized Dividend / Current Market Price
- Dividend Payout Ratio = Dividend Per Share (DPS) / Earnings Per Share (EPS)

DIVIDEND PER SHARE = Dividend Declared % x Face Value = 290 % x 10 = 29
DIVIDEND PAYOUT RATIO = Dividend Per Share / Earnings Per Share = 29/23.76 = 122.05 %
DIVIDEND YIELD = Dividend Per Share / Current Market Price = 29/347 = 8.35 %
Investors must note that dividend is denoted as a percentage of the face value of the stock and not the market price.
Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is a prominent tool used by investors to scan companies when there is a downturn in the stock markets as annual dividend payments act as a cushion against a free fall in the stock prices.
Historically, a high dividend yield has been desired by investors as the investors know what their minimum return on investment would be apart from any capital appreciation.
Click Here to view companies who constantly pay dividends or have a good dividend yield.
By the way, do you know that many investors focus on generating passive income by investing in only dividend-paying stocks? However, there are some key points to keep in mind while investing in stocks that have declared a dividend. Let us learn this in the next section.
Investing in Dividend Paying Stocks
What does an Investor need to keep in mind while buying a company that has declared Dividend?
There are some important dates which the investor needs to be aware of before investing in a company that has recently declared a dividend.
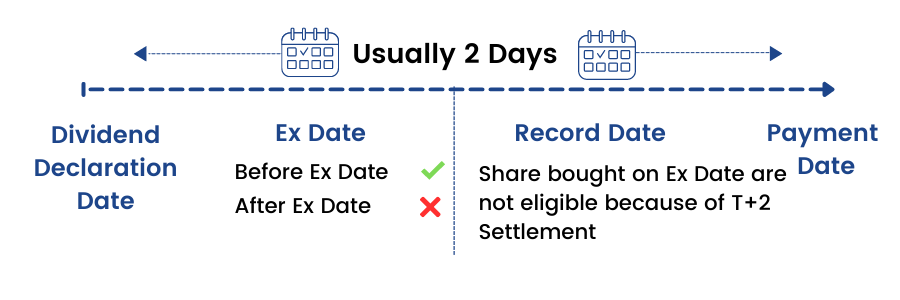
Dividend declaration date: This is the date on which the board of directors announces the consideration of dividend. Subsequently the shareholders approve the dividend in AGM or through postal ballot (generally, the board of directors have shareholder's pre-approval till a certain level of dividend payout)
Ex-dividend date: On (and after) this date the security trades without its dividend. If an investor buys a stock (cum dividend) before the ex-dividend date he would be eligible for the dividend but if the stock is bought on or after the ex-dividend date, the investor would not qualify for the dividend. The ex-dividend date is usually fixed one day before the record date.
Record date: This is the date on which the company looks at its records to ascertain the shareholders eligible for dividend. An investor name should be in the record of shareholder register to avail the benefit of dividend
Dividend payable date: On this date, the company credits shareholders' account with the dividend amount
However, dividend and dividend yield should be only taken into consideration if the company posts healthy financials. Companies paying a special dividend or a one-off payment due to an exceptional gain which is not expected to be repeated in future should be excluded from this group.
Stock Splits
Earlier in this module under the purposes of corporate actions, we read about stock splits impacting the price of the shares. Let us discuss the concept of stock split in this section.
What is Stock Split?
A stock split is a corporate action which splits the existing shares of a particular face value into smaller denominations so that the number of shares increases, however, the market capitalization or the value of shares held by the investors post-split remains the same as that before the split.
For e.g. If a company has issued 1,00,00 shares with a face value of ₹10, the current market price being ₹100, a 2-for-1 stock split would reduce the face value of the shares to ₹5 and increase the number of the company's outstanding shares to 2,00,00 (1,00,00* (10/5)). Consequently, the share price would also fall to ₹ 50 so that the market capitalization or the value shares held by an investor remains unchanged. It is the same thing as exchanging a ₹100 note for two ₹ 50 notes; wherein the value remains the same.
Let us see the impact of this on the shareholder: - Let's say company ABC is trading at ₹4 and has 1 million shares issued, which gives it a market capitalization of ₹ 4 million (₹ 4 x 1 million shares). An investor holds 400 shares of the company valued at ₹1,600. The company then decided to implement a 4-for-1 stock split (i.e., a shareholder holding 1 share, will now hold 4 shares). For each share shareholders currently own, they receive three additional shares. The investor will therefore hold 1600 shares. So, the investor gains 3 additional shares for each share held. However, this does not impact the value of the shares held by the investor since post-split, the price of the stock is also split by 25% (1/ 4th), from ₹ 4 to ₹1, therefore the investor continues to hold ₹1,600 worth of shares. One must note that the market capitalization stays the same - it has increased the number of stocks outstanding to 4 million while simultaneously reducing the stock price by 25% to ₹ 1. The true value of the company hasn't changed. An easy way to determine the new stock price is to divide the previous stock price by the split ratio. In the case of our example, divide ₹4 by 4 and we get the new trading price of ₹ 1. If a stock were to split 5-for-2, we'd do the same thing: 4/ (5/2) = 4/2.5 = ₹ 1.6.
Discover the secrets of stock splits in our 'Stock Market Made Easy' course. Enroll now for simplified stock market mastery!
An Example:

Colloquially speaking, a stock split can be thought of as cutting a cake into smaller digestible slices. The premise is simple - nothing really changes whether you eat two small pastries instead of a large one.
Reasons for Stock Split & Implications of a Stock Split
It is natural for one to question the rationality behind a stock split. Fundamentally, there is no effect whatsoever. However, companies cite some other reasons:
- One among them is that participation in the company's shares gets lower because investors shy away at an abysmally high price. Generally small and retail investors have a mentality that shares in smaller denominations are cheaper and thus they keep away from an overpriced stock. This leads to reduced investor interest.
- The second reason would be to improve liquidity in a company's stock by increasing the number of outstanding equity shares.
Example: If a stock is quoting at a market price of ₹1000 and has a face value of Rs 10, a stock split of 10:1 will bring the stock price down to ₹100 and make it more attractive & affordable for investors.
Right Issue
Similar to a stock split, a right issue is also a part of corporate action. Let us learn everything about rights issues in this section.
What is a Right Issue?
A right issue is basically a way through which a listed company raises additional funds from existing shareholders. Rights Issues are primary market activity. The company implementing the rights issue is offering additional and/or new shares but only to existing shareholders. Existing shareholders are given the right to purchase or receive these shares before they are offered to the public.
A rights issue takes place in a form wherein the existing shareholders are given the right to subscribe to additional shares normally at a discount to the prevailing market price of the stock. The shareholders receive this right by virtue of being stakeholders in the company. They can also sell their rights for a consideration to others if they do not wish to subscribe for additional shares. In essence, rights are freely traded & transferrable.
A rights issue is contemplated by equity shareholders in the view that it is a way to raise money from the market via equity dilution. Shareholders must carefully examine the purpose behind raising funds and whether or not promoters/promoter groups are subscribing to the issue.
Let’s understand this concept better with the help of an example –
Reliance Industries Ltd. has proposed the right issue in the ratio of 1:15.
This means Reliance Industries Ltd.’s shareholders can subscribe to 1 equity share for every 15 equity shares held by eligible shareholders as on the record date. The right issue price is ₹1257. It is about a nearly 14% discount on the company stock’s price of ₹1466 as of April 30, 2020.
Let us suppose investor A currently holds 90 shares of Reliance Industries, which were brought at a price of ₹1,400
The company set a conversion rate of 1:15, meaning that investor A can buy 1 discounted share for every 15 that he owns on the record date. As a result, the investor could buy 6 (90/15) more shares for ₹ 1257.
So now his cost for a total of 96 shares would be:
(90*₹1400) + (6*₹1257)
= ₹ 1,33,452
Cost of one share: 1,33,452/96
=₹ 1,391
Now, his actual cost price for 90 as well as other shares comes to ₹1,391 Vs the closing price at ₹1,466.
Should you Invest in the Rights Issue of Shares?
Continuing with our previous example, Investor A is entitled to subscribe for 6 right shares in lieu of his shareholding. Investor A’s demat account will be credited for 6 RE’s (Rights Entitlement) as a proof of ownership. Now, let us look at the three alternatives available to the investor:
First case – One can exercise his rights by subscribing to additional equity shares of Reliance Industries.
Second Case – One does not want to apply for the rights issue so he/she does not exercise his rights.
Third Case – One can renounce his/her rights by selling his Rights Entitlement (RE) in the open market within a stipulated time period. The base price aka the minimum price below which the value of RE must not fall is the PV(Market Price of stock-Rights Issue Price)
Other market participants who do not own equity shares of the company, can participate in the rights issue by purchasing RE’s from the open market.
Why do companies go for Rights issue?
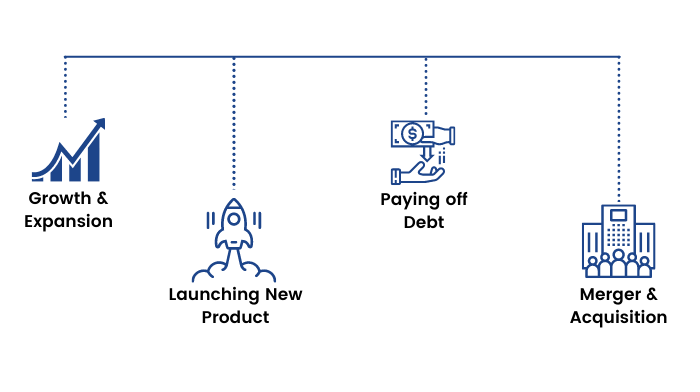
Companies go for the rights issue of shares to raise funds for:
1.Growth and Expansion.
2.Launching new products.
3.Paying off debt.
4.Taking over another company (Acquisition).
An investor should check out the reason for the rights issue before opting for it. He should also make sure the company has strong earnings visibility coupled with visionary management.
Advantages of rights issues:
- The shares are offered to the shareholders at a discounted price. So, it is an opportunity for the existing shareholders to increase their stake in the company at a lower price thus decreasing their holding price average for the company.
- For the company, the Right issue is one of the best ways to raise capital without incurring additional debt from the banks on high-interest rates thus cutting on the Finance cost for a Company.
Disadvantages of rights issues:
- If the shareholders do not subscribe to the rights issue, then the company may fail to achieve its target.
- Promoters can raise more money from an FPO as they can raise rights only in proportion to their existing Equity value.
- If a stronger Balance Sheet company is going for the right issue of the shares, then it goes on to create a negative market sentiment for that particular company. It is assumed that the company is struggling to run its business operations smoothly.
- Due to rights issue dilution of Equity happens thus ones who do not want to subscribe to the rights find their percentage of holding getting reduced due to allotment of new shares.
- There is a time lag between rights shares issued and transferred to holders' accounts thus the same percentage of discount might not be available while selling the rights shares.
How do you apply for a rights issue?
There are two ways to apply for a rights issue:
1.If your bank supports ASBA (Application Supported by Blocked Amount), you can apply online just like an IPO.
2.If your bank doesn’t support ASBA, then you would have received a courier of the Composite Application Form (CAF) from RTA (Registrar and Transfer Agent) of the company.
Buyback Shares
Earlier in this module under the purposes of corporate actions, we read about buybacks impacting the price of the shares. Let us discuss the concept of buyback in this unit and also reasons for buyback in the subsequent unit of this module.
What do you mean by Buyback of shares?
Buybacks are a method through which a company buys its own stock from investors. A buyback reduces the company’s cash holdings (assets) as well as the total number of outstanding shares.
Buybacks are normally done at a premium to the prevailing market price and thus rewards the shareholders. This also induces other investors to enter into the stock to take advantage of the arbitrage opportunity available and thus drives up the stock price.
Also, buybacks are perceived as a positive development since it reflects the renewed conviction of the promoter in the business. The stock purchased by the company is extinguished after successful completion of the buyback, thus reducing the equity base of the company. The promoter holding is expected to go up (generally, promoters do not participate) as they effectively own a larger percentage of the total outstanding equity shares of the company. Also, promoters now have a greater say in the decision-making of the company (more voting rights).
The company has to disclose the pre and post-buyback holdings of the promoters. To ensure completion of the buyback process speedily, the regulations have a stipulated time limit for each step.
For example, in the case of purchases through stock exchanges, a buyback offer should not remain open for more than 30 days. The verification of shares received in buyback has to be completed within 15 days of the closure of the offer. The payments for accepted securities have to be made within 7 days of the completion of verification and bought back shares have to be extinguished within 7 days of the date of the payment.
Method of buyback of shares
1.It can be done on a proportionate basis by the existing shareholder through the offer.
2.Buyback of shares can also be done in the open market through stock exchange via book building process.

SEBI guidelines on buyback of shares
SEBI’s guidelines on buyback of shares are as follows: -
1.The pre and post shareholding by the promoters needs to be disclosed by the company.
2.The company is not allowed to issue the same class of shares for the upcoming year post buyback.
3.The shares bought back have to be reduced from the number of outstanding shares of the company within seven working days.
Under the SEBI Buyback of Securities Regulation 1998, a company is permitted to buy back its shares from:
1.Existing shareholders on a proportionate basis through the offer document
2.Open market through stock exchanges using the book building process
3.Shareholders holding odd lot shares
Impact of buyback of shares
1.The number of shares outstanding goes down due to the buyback of shares.
2.Buyback leads to an increase in earnings per share (EPS). As it reduces the company’s outstanding shares, the impact is clearly evident in per-share measures of cash flow and profitability.
3.It also leads to an increase in the company’s stock price. Generally, the buyback is looked upon as a sign of increased confidence in business prospects from the promoters.
Reasons for Buyback Shares
What are the reasons for buyback of shares?
1.Buyback helps to reduce the threat by the shareholders who may be looking for a controlling stake in the company.
2.The company may also use buyback for the de-listing of shares.
3. Companies may go for buyback in poor market conditions to support falling prices, as they believe the share price is undervalued.
4.When the company has abundant idle cash & there are not enough growth opportunities available.

Advantages of buyback
1.It prevents a decline in the value of a share by reducing the supply of the Shares in the market and also due to the reduction in outstanding shares the Earnings per Share (EPS) of the company improves.
2.It is also used strategically by the management to show its confidence in the company and to send a message that the stock is undervalued.
3.Helps the company use its excess cash lying idle due to lack of opportunities.
4.If promoters do not participate in the buyback process, it increases their holdings, thus strengthening their hold over the company & preventing potential takeovers by rivals.
5.When a company pays dividends, all shareholders receive cash as per their shareholding, whether they need it or not. However, shareholders are free to decide if they want to tender their shares in the buyback process.
Disadvantages of buyback
Buybacks may indicate a lack of profitable opportunities for the company to invest in, which may send a bad signal to long-term investors looking for capital appreciation.
The entire process is time-consuming and requires a lot of disclosures to the stock exchanges and approvals from regulatory bodies. It also becomes an expensive affair for the company as it is usually done at a premium to the market price.
Mergers and Acquisition (M&A)
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) play an important role in the corporate action of a company. Here in this unit, let us learn how?
A merger is a corporate strategy that involves the consolidation of two or more companies to operate as under the legal banner of a single legal entity. A share swap ratio is decided on the basis of market prices of both the companies (if the target is a listed company). Shareholders of the target company are eligible to receive shares in the acquiring company if the merger is successful.
If a company undergoes a merger, it may indicate to shareholders that the company has confidence in its ability to take on more responsibilities. On the other hand, a merger could also indicate a shrinking industry in which smaller companies fall prey to market stalwarts.
In the case of an acquisition, however, a company seeks out and buys a majority stake of a target company's shares; the shares are not swapped or merged. Acquisitions can often be friendly but also hostile, meaning that the acquired company does not find it favourable that a majority of its shares were bought by another entity.
A situation of M&A can turn out to be favourable or unfavourable for the minority shareholder and has both the faces to it. If the consideration paid for the acquisition turns out to be favourable then it is beneficial for the shareholders of both the companies. However, if the acquisition cost turns out to be much higher than the market value of the company then it is not viewed positively by the minority shareholders of the acquirer company but positively by the acquired company.
Features of Mergers/Acquisitions
- A merger is a corporate strategy that involves the consolidation of two or more companies to operate as a single legal entity. It is friendly in nature i.e., both the parties agree to the terms of the merger
- An Acquisition or Takeover refers to a company buying a majority/controlling shares of another company in order to obtain control over the same. Acquisitions can be friendly or hostile in nature.
- Since the target company is usually bought at a premium, the share prices increase in the short term.
- Acquirer’s future is uncertain and thus there is a fall in the share prices of the acquirer company in the immediate term
- Future status of share prices depends upon the synergies from the merger
Examples:

Demerger - A demerger occurs when a conglomerate that has varied business interests under a single entity hives off one or more units into a separate legal entity. Usually, the parent company hives off its non-core business segments under a different entity to improve focus on its core business and also unlock value of the other businesses which are embedded with the company. Demergers are generally interpreted positively by market analysts. Herein also, a share swap ratio is decided on the basis of which shareholders in the parent company get additional shares in the subsidiary company.
For example: - In 2009, the boards of Reliance Industries (RIL) and Reliance Petroleum (RPL) approved the demerger of the two firms, with a ratio of one RIL share for 16 RPL shares.
In 2015, the Board of Max India Ltd approved a Corporate Restructuring plan to split the company through a demerger, into three separate listed companies with three separate business verticals ‐ life insurance, health and allied businesses and manufacturing industries. The company split into three entities – Max Financial Services Ltd with the insurance business, Max India Ltd with the healthcare and allied businesses and Max-Ventures and Industries Ltd with speciality packaging film business.
Bonus Issue
In Unit 2 of this module, we have learned that bonus issues are a way to distribute dividends by the companies to their shareholders. Therefore, let us elaborate on the concept in this section.
What is a bonus issue?
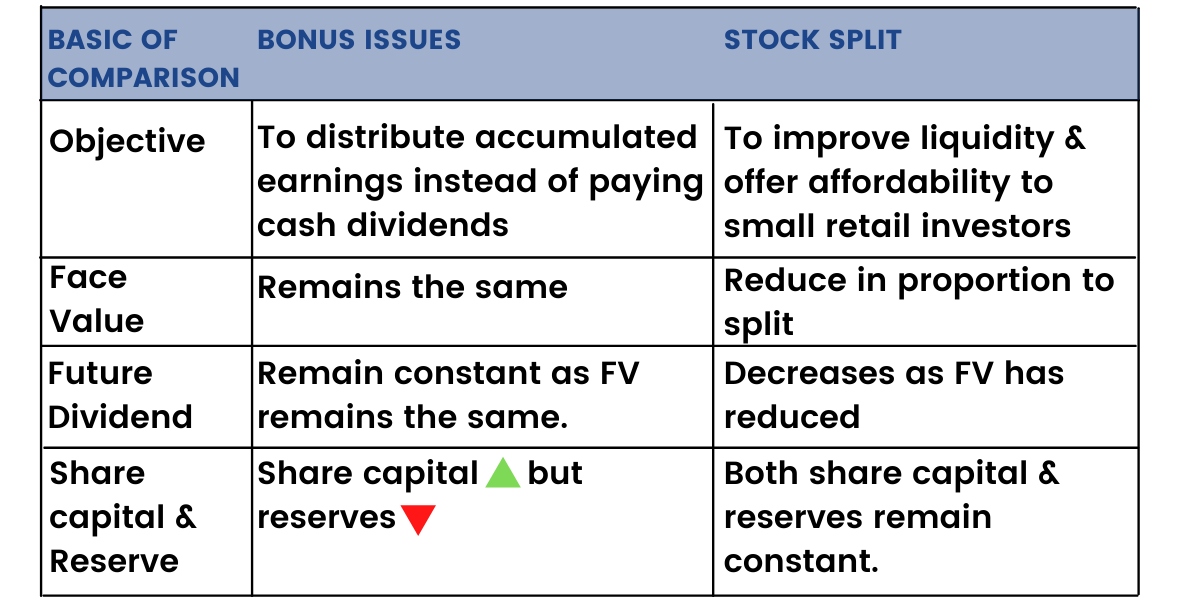
A bonus issue, also known as capitalization issue, is where the company offers additional shares to the existing shareholders without any consideration. The free shares are issued in proportion to their existing shareholding in the company and in the ratio decided by the company.
For example, in a 1:2 bonus issue an existing shareholder is eligible to receive one extra share for every two shares of the company held by him on the record date. In case a person holds an odd number of shares, the difference is cash-settled .
A bonus issue signifies no fundamental change in the company; neither does it make it a lucrative investment since the stock price is expected to go down in a similar proportion. The company simply capitalizes its general reserves (retained earnings). Thus, there is no net effect on the company.
Issuing bonus shares increases the number of shares which leads to a decrease in the stock price of the company in proportion to the bonus ratio. It makes the stock attractive to retail investors who hesitate to invest in high priced companies.
As an illustration, let us assume that ABC Corporation has 1000 outstanding equity shares. It announced a 1:1 bonus issue, when the market price of its stock was ₹1000. After the bonus issue, the stock is expected to go down to ₹500. Meanwhile, the number of total outstanding shares will double to 200.
Usually, a company announces a bonus issue as a means of rewarding its shareholders. A bonus is also viewed as a stock dividend where the cost for the company is less than the cost incurred in giving a cash dividend.
The face value of the stock remains the same in a bonus issue unlike a stock split and hence the only way the investor can make gains is if the dividend per share remains the same as-the previous year after the share goes ex-bonus
Issuing a bonus is just like cutting a cake into smaller portions. The total size of the cake does not change no matter how many times you cut it.

Bonus Issue Vs Stock Split
Impact of Corporate Actions on Financial ratios
Here in this unit, we will discuss the impact of different corporate actions on the financial ratios of the companies. If you are unaware of the concept of financial ratios, you can read our ELM school module on 'Ratio Analysis.' Click here.
Now, let us continue one by one.
1)Buyback of Shares
When the company purchases its own shares, then the outstanding shares in the market get reduced and hence the investors stake increases as the number of shares have reduced in the market.
Buybacks can be performed either through a tender offer route or through the open market.
Now let us understand how the Buyback of shares affects the financial ratios of the company.
Impact on Earnings Per Share (EPS):
EPS is calculated by dividing the net income by the total outstanding number of shares during the year. Since the company extinguishes the shares bought back, the EPS tends to increase.
Let us understand this with the help of an example:
Company – XYZ Ltd
Outstanding Shares – 100 crore shares at the beginning of the year.
Net Income – ₹500 crores,
EPS = ₹5 (500/100).
Buyback Shares = 10 crore shares
Hence the outstanding number of shares post buyback is 90 crores (100-10).
Now the Revised EPS is ₹5.55 (500/90).
Several valuation metrics incorporate EPS in their calculation & hence the stock is positively re-rated.
Impact on debt-to-equity ratio:
Debt to equity ratio measures the financial leverage of the company.
It is calculated by dividing the Total debt by the Total Equity during the year
It represents the proportion of debt a company takes to finance its operation.
Buyback of shares reduces the equity of the company.
Since, the equity of the company is reduced it increases the debt-to-equity ratio of the company.
For example, a company has debt amounting to ₹50 crores.
The company’s equity is ₹100 crores before the buyback.
The company has undertaken buyback worth ₹10 crores during the year which reduces the equity of the company to ₹90 crores (100-10).
Hence the debt-to-equity ratio deteriorates from 0.5 (50/100) before buyback to 0.55 (50/90) post buyback
Impact on book value per share:
Book value per share is derived by dividing shareholder’s equity by the total outstanding shares.
A company’s book value per share will decrease after a share repurchase if the market price per share was greater than the book value per share prior to the repurchase and vice versa.
This is explained in two situations below-
For example,
Case 1:
XYZ is a company with 1,00,000 shares outstanding.
The shareholder equity value of the company is 15,00,000 and hence the book value computed is ₹15 (15,00,000/1,00,000).
Now let us assume that the company buybacks 10,000 shares @₹10 per share amounting to ₹1,00,000.
Post the buyback of shares, the shareholders equity value of the company has reduced to ₹14,00,000 (₹15,00,000-₹1,00,000) and the book value per share has increased to ₹15.56 (₹14,00,000/₹90,000).
Thus, this impacts a company positively as it’s worth has increased.
Case 2:
XYZ is a company with 1,00,000 shares outstanding.
The shareholder equity value of the company is ₹8,00,000 and hence the book value computed is:
(₹8,00,000/₹1,00,000) = ₹8
Now let us assume the company buybacks 10,000 shares @₹10 per share amounting to ₹ 1,00,000.
Post the buyback of shares, the shareholders equity value of the company has been reduced to ₹7,00,000 (₹8,00,000-₹1,00,000) and the book value per share has decreased to ₹7.77 (₹7,00,000/₹90,000).
In this case, the book value per share was higher before the buyback.
The effect of a corporate action should always be measured before making any investment decision.
2)Rights Issue
The rights issue is an offering to the existing shareholders of the company which makes them eligible to buy additional shares in the company at a discounted price to the prevailing market price of the shares.
The rights issue on shares can be subscribed by the existing shareholders as proportionately to the number of shares being held by them on the record date. Other market participants can also take part in rights issues by purchasing Rights Entitlements from the open market.
Impact on Debt-to-Equity Ratio:
Rights issue of shares improves the debt-to-equity ratio of the company.
Debt-to-equity ratio is computed by dividing the debt value of the company by total equity of the company.
When the company issues right shares, the company’s equity value increases.
Therefore, the debt-to-equity ratio improves since the company has raised money through the issue of shares (equity).
For example, XYZ Ltd has 100 outstanding shares & ₹200 in long-term debt.
The company plans to issue right shares in a ratio of 1:5 to its existing shareholders to finance a new project.
Post issue, The debt-to-equity ratio will improve from 2(200/100) to 1.66 (200/120).
Impact on EPS:
EPS is computed by dividing the net income by the total outstanding shares of the company.
In case of rights issues, the number of shares increases and hence the earnings per share is reduced.
Moreover, to keep the EPS constant post right issue, the company’s profit should increase to a greater extent in the future to compensate for the additional shares.
For Example, XYZ Ltd has a net income of ₹10 crores during the year. The company has 1 crore shares outstanding during the year. The company has issued rights shares in a ratio of 1:10 to the existing shareholders. As a result, the total number of outstanding shares increases to 1.1 crores.
Therefore, the EPS of the company has reduced from ₹10 (10/1) to ₹9.09 (10/1.10) post rights issue
Hence, The EPS gets negatively impacted due to rise in the number of outstanding shares.
3)Bonus Shares
Bonus shares are fully-paid up shares issued free of cost to existing shareholders in a certain ratio.
Bonus shares are issued by companies to capitalize on their free reserves. Companies share their retained earnings with their shareholders in the wake of absence of any capex or expansion in the near future.
Impact on EPS:
EPS is computed by dividing the net income of the company by the total outstanding number of shares.
In case of bonus issue, the company issues additional shares to its existing shareholders on a proportionate basis.
Therefore, bonus issue of shares reduces the EPS of the company.
For example, XYZ Ltd has reported a net income of 10 crores for the year and has 1 crore shares outstanding during the year.
The company issues bonus shares in a ratio of 1:1 during the year.
The bonus shares are shares that are offered free of cost to the existing shareholders and hence it only increases the number of shares outstanding.
Hence, the EPS of the company during the year falls from ₹10 (10/1) to ₹5 (10/2) post issue of bonus shares.
Summarizing what we just learnt:
- Buyback of shares improves the earnings per share of the company.
- Buyback of shares adversely impacts the debt-to-equity ratio of the company.
- Buyback of shares impacts book value per share both positively as well as negatively
- Rights issue of shares positively impacts the debt-to-equity ratio of the company.
- Rights issue of shares negatively impacts the earnings per share of the company.
- Bonus issue of shares adversely impacts the earnings per share of the company.


