Currency Markets
What is Currency?
To understand currencies, we need to go back in time and take a dive into our history.
Before currencies came into the picture, there was something called the “Barter System”. Here, people exchanged goods for other goods. For example, suppose a farmer “A” harvests wheat and wants 1 kg rice. Similarly, another farmer “B” harvests rice and wants 1 kg of wheat in return. The two farmers can exchange goods with each other.
However, the problem with the barter system is scalability, i.e., it is very difficult to measure what the exact quantity of wheat farmer “A” needs to offer that will be equal to 1 kg of rice. Every commodity which is available in the market does not represent the same utility values, meaning a person may desire water more than they desire potato.
Soon people realized the problems with this system and came up with what is known as "the metal era". Here, people exchanged goods for a certain amount of metal which could be gold, silver, etc. This system proved to be better than the barter system, but is not an optimal solution because when people started depositing gold and considered it as a "safe haven currency", it became known as the “paper currency”.
Banks were formed, people started depositing their money in them, different countries started to represent themselves by their currencies. People also started to understand that it is not optimal to produce everything on their own, and, it may be cheaper to import some of the commodities, which also meant that merchants had to pay a currency that was acceptable in terms of the country that they were exporting the goods from.
In the 1870s, countries agreed to value their currency with other countries using gold as the benchmark for valuation. As per this process, central banks issue paper currency and hold an equivalent amount of gold in their reserves. As countries disagreed on the value of the currencies that the other country had set up, this led to the creation of currency markets, where the markets decide the value of each currency independently. Therefore, the value of each currency against another is derived from the exchange rate.
To put it simply, when money is branded it is called 'currency'. Each country has its own 'brand'. Whenever there is a cross- border trade, a need to exchange one brand of money for another is developed, and this exchange of currencies is known as "foreign exchange" or "forex".
How To Invest In Currency?
People invest in currencies because of various reasons. Unlike the stock market, currency markets are way bigger and government bodies, like the RBI, banks, also trade in the currency. The reasons for trading differ, for example, RBI trades to provide a hassle-free and timely flow of credit into the markets, or to improve the balance of trade of their country or to control inflation, the reasons are plenty.
There are two ways in which we can invest in a currency as investors:
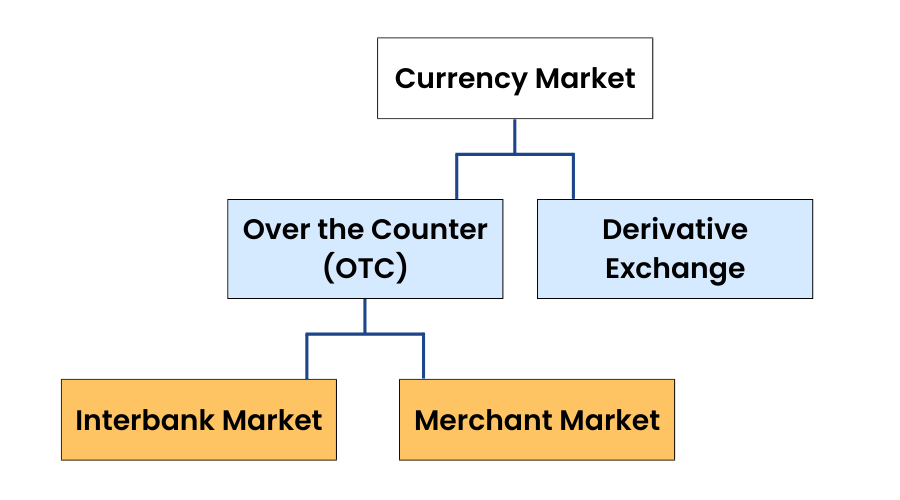
1.OTC (Over the Counter) Markets
An over-the-counter market is a market that is not regulated by an authority. In these types of markets, dealers act as market makers by quoting the buy and sell prices. These markets are generally very illiquid, meaning an investor has to be compensated with a liquidity premium in their investments.
OTC markets are also generally very less transparent and are subject to fewer regulations. Lower entry costs are an added advantage of the OTC markets.
There are two subcategories of OTC markets:
a)Interbank Market- The interbank market is a global market for financial institutions to trade currencies between themselves.
b)Merchant Market- Merchants help businessmen to start a business and help to raise finance. They provide consultancy to its clients for financial services.
2.Derivative Exchanges
Currency derivatives are futures and options contracts that trade on the exchange. Derivative contracts are generally more transparent and are traded on a real-time basis. Currency derivative exchanges are similar to stock exchanges. We can trade currencies at NSE and BSE exchanges.
Currency derivatives are useful in the following ways:
- Hedging: Traders and Investors face risk associated with the prices of underlying assets and use derivatives to reduce their risk.
- Arbitrage: Traders try to find a mispriced security in two different markets and profit from it.
- Speculating: Traders try to predict the future movements in the price of underlying assets and based on the view, take positions.
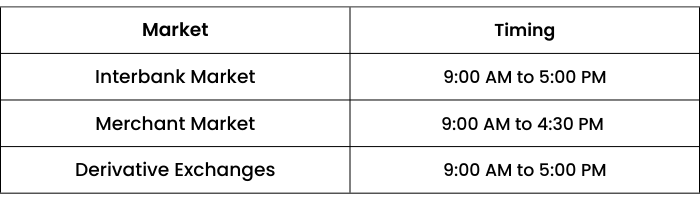
What are the Currency Market Timings in India?
Ready to master currency investment? Enroll now in 'Stock Investing Made Easy' and expand your financial portfolio confidently!
Currency Terminologies
Before we move forward with this module, we should know about some basic terms which are related to currencies.
What is an Exchange Rate?
An exchange rate between two currencies specifies how much one currency is worth in terms of the other. For example, an exchange rate of ₹67 to USD means that ₹67 is worth the same as 1 USD.
An exchange rate quotation is given by stating the number of units of "term currency" or "Quote currency" that can be bought in terms of 1-unit currency or Base Currency. Thus, in the quotation on the NSE currency trading terminal which says that the USD/INR exchange rate is 67.40 INR per USD, the term currency is INR and the base currency is USD.
Bid price: is the price which potential buyers are willing to pay
Ask price: also known as the 'offer price', is the price at which sellers are willing to sell
Bid Ask Spread: is essentially the difference in price between the highest price that a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price for which a seller is willing to sell an asset
Typical exchange rate quote is like USDINR = 67.4150/75
Bid-Ask Spread is (67.4150-67.4175) = 0.0025


Source: NSE India
What is the Spot Exchange Rate?
A spot exchange rate is the current price level quoted in the market for the immediate delivery of one currency to another. The standard settlement convention for Foreign Exchange Spot trades is T+2 days, i.e., 2 business days from the date of trade execution. An exception is the USD/CAD (US–Canadian Dollars) currency pair which settles T+1.
What is Forward Exchange Rate?
The forward exchange rate refers to an exchange rate that is traded and quoted today but the payment and delivery of that contract are on a specific future date.
What is Forward Premium?
A currency is said to be trading at a premium in the forward market if its value in the forward market is higher than in the spot market. For example, the spot exchange rate for USD/INR is 44 and if a 6-month forward contract of USD/INR is trading at 44.5, then it is said that USD is trading at a premium of 50 bps against INR in the forward market.
What is Forward Discount?
A currency is said to be trading at discount in the forward market if its value in the forward market is lower than in the spot market. For example, the spot exchange rate for USDINR is 44 and if a 6-month forward contract of USDINR is trading at 43.5, then it is said that USD is trading at a discount of 50 bps against INR in the forward market.
What is the Spot Forward Relation?
In international markets for fully convertible currencies, the forward premiums/discounts are purely a function of the difference between interest rates of the 2 countries that have fully convertible securities. Under covered interest rate parity in a two-currency pair, the currency of the country with a higher interest rate than that of the other will trade at a discount to the other currency.

Here,
F = Forward Rate
e = Spot Rate
if = Interest Rate in the term currency
i = Interest rate in the base currency
For example, On June 30, the spot USD/INR rate was 67.42. The US interest rate is 0.50% and Indian interest rate is 6.50%,
E=67.42; Idc = 0.065; Ifc = 0.005.
F = 67.42(1+0.065) / (1+0.005)
= 71.4450.
Therefore, the forward rate will be 71.4450 for 1 USD.
In the case of India, this stated spot forward relation between USD/INR does not work completely because India follows a managed floating exchange rate regime. As stated, RBI from time to time trades in the market to maintain a stipulated level of the exchange rate to support both the exporters and importers.
What are Swaps?
A foreign exchange swap is a simultaneous sale and purchase, or vice versa, of an identical amount of one currency for another with two different values. The two commonly used swaps are:
- Interest rate swaps: This involves swapping only the interest rate between 2 parties of similar currency.
- Currency swaps: This involves swapping both interest and principal between 2 parties, with the cash flows of 2 parties being different.
Concepts Of Currency Markets
Till now, we have learned the concept of currency and why it is so important. As we have discussed a few ways to invest in currency markets, there is more to learn about before jumping into the trades. There are numerous concepts that must be learned to understand the complexities of currency. Let's discuss them here:
What is a Cross currency rate?
A cross rate is a foreign currency exchange rate between 2 currencies that is valued against a 3rd currency.
For example,
If the USD/INR exchange rate is valued at 67.4150/75, and,
If EUR/USD is valued at 1.1132/42,
Then, the EUR/INR spot rate can be calculated by multiplying the two rates so USD gets cancelled out and we get 75.1125/75.
Thumb Rule:

What is Triangular Arbitrage?
In triangular arbitrage one currency is traded for another currency, which is traded for a third currency, which in turn, is traded for the 1st currency.
Triangular arbitrage opportunity arises when the currency direct quotes are not in alignment with the cross-exchange rates.
For example, the following are available in the foreign exchange market:
GBP/INR: 89.6775
USD/INR: 67.4150
GBP/USD: 1.33
- Step1: Buying Indian rupee with 1 million GBP to get INR89.67 million.
- Step 2: Convert INR into USD: 89.67/67.41= USD 1.3302million.
- Step 3: Sell USD to GBP: 1.3302/1.33= GBP1.0002million.
Hence, the arbitrage gets a net gain.

What is Calendar Spread Trading?
Calendar spread in currency futures is the difference between the prices of two currency futures contracts with different expiry months but with the same underlying currency pair.
Usually, traders profit by identifying the relative movement of, say, the near-month futures contract price with the price of the subsequent month's futures contract.
Before we discuss this we need to know two concepts of Contango and Backwardation.
- Contango: When the far-month futures contract price is greater than the near-month contract price, the market condition is usually referred to as ‘normal’ or contango.
- Backwardation: When the far-month futures contract price is less than the near-month contract price, the market condition is known as ‘inverted’ or backwardation.
A trader can take opposite positions between futures contracts of different expiry months with the expectation that the spread either increases or decreases.
In a contango market, if the trader expects the spread differential to increase between the January and February MCX-SX USD/INR futures, it would be prudent to take a short position in the January contract and simultaneously take a long position in the February contract.
On the other hand, if the spread differential is expected to decrease, the trader should take the reverse positions.
For example:
10 lots of July USDINR contract, which is trading at Rs. 67.5800 are bought and10 lots of August USDINR contract, which is trading at ₹67.9600 are sold.
The spread works out to Rs. 0.38 (67.9600 – 67.5800).
So, the spread profit =spread x number of lots x lot size
= 0.38 x 10 x 1,000
= ₹3,800
What are currency options?
An option is a derivative contract that gives the buyer, the right to exchange a product at a pre-specified price on a specific date. Currency options have the same concept, as it gives a buyer the right to purchase or sell a currency on a specified date at a specified price.
Currency options can be used by corporations or individuals to hedge the uncertainty involved when dealing with foreign exchange rates. Additionally, currency options can be used for speculative purposes.
There are two basic types of options:
A)Call Option – The buyer of a call option has a right, but not an obligation to purchase a currency in exchange for a call premium.
B)Put Option – The buyer of a put option has a right, but not an obligation to sell a specific currency at a predetermined price. For this, the buyer needs to pay the put premium initially to purchase the option.
The concepts that we have learned so far are extremely important while trading the currency markets. As explained through various examples, the value of a currency is not fixed; rather, they change. Why so? There are multiple factors that we will learn in the next unit of our module.
Factors Affecting The Currency Markets
A stock's value is based on the expected future earnings, as the expectation increases, the value of that stock goes up. Exchange rates, on the other hand, are affected by a completely different set of factors, out of which, one of the most important factor is a currency's supply and demand. The currency markets of the world can be viewed as a changing mix of current events. The volatile nature of current world events, and, the constant shifting of supply and demand can lead the price of a currency to always be on the move. Forex is the most affected market in the world because of many external factors.
Supply and demand for a currency are influenced by several factors. These falls into three categories:
- Political conditions
- Market psychology
- Economic factors
Political Conditions:
A country’s political condition plays a vital role in its currency movements. An economy faces a negative impact at times of political turmoil, and if a nation has elected a new government that is seemed as "economically friendly" favorable economic and trading conditions may result. Political events both inside and outside a country can have a huge impact on a nation’s economy and currency.
Market Psychology:
To explain this factor we will take the example of Brexit and how it impacted:
In recent years, Brexit has been a very major event. The Great Britain Pound fell by 8.64% when this news occurred, and is a very big percentage while dealing in currencies.
Brexit as the name suggests is Britain exiting the European Union. On June 23rd, 2016, the citizens of Europe were told to vote for or against Britain exiting the EU. The results were a bit shocking because almost everyone in the world believed that Britain would stay in the EU.
When the UK decided to exit the EU, there were both political as well as economic impacts. Considering the magnitude of the event, there was a lot of uncertainty, and panic among the people, which led to investors being bearish and this is what led to the crashing of GBP to a 31 year low.
Economic Factors:
The government's economic policy and conditions can have a big impact on its exchange rate. The economic policy includes a government’s fiscal policy, budget policies, government spending, etc. Monetary policy is controlled by a nation's central bank (RBI) and includes the interest rate and the supply of currency.
The following are some of the economic factors that affect the currency markets:
- Deficits & Surplus:
The wider a nation's deficit, the lower its currency and trade value, and vice-versa.
- Trade levels and trends:
The more a nation is involved in trades, the higher the demand will be for its currency to perform these trades, which increases the value of its currency and vice versa.
- Inflation:
The higher a nation's inflation rate, the lower the value of its currency. CPI or the Consumer Price Index is an index that measures inflation.
- Economic figures and reports:
Key economic data such as GDP (gross domestic product), employment, and unemployment levels, goods sold, can offer an insight into a nation's growth and health. Economic figures that people pay constant attention to include, inflation, (un)employment, trade figures, and money supply. Country's economic reports, outlining its GDP (Gross Domestic Product), NNI (Net National Income), GNI (Gross National Income), NNP (Net National Product), GNP (Gross National Product) are also important variables. Commonly, the healthier a country's economy, the better its currency performance will be, which will then generate a higher demand for it.
Inflation And Currency
Previously we have learned that the higher a country's inflation, the lower the value of its currency. But why is that so? What is the relation between inflation and currency? Let's discuss:
In the long run, the most important factor influencing exchange rates is inflation. The relation between exchange rate and inflation, while other factors remain constant is known as the Purchasing power parity (PPP). Inflation leads to a loss of purchasing power. Thus, as per PPP, if inflation in India (say 10%) is higher than that of the US (say 4%), USD should appreciate against INR in the long run to the extent of the inflation differential. The rationale behind PPP is the law of one price which must hold good to prevent commodity arbitrage.
For example, we'll take 2 fictional countries A & B. Suppose that on January 1st, 2020, the price for every good in each country is identical. Thus, a pen that costs $20 in country A costs 20rupees in country B. If PPP holds, then 1 Dollar will be worth 1 rupee, otherwise, we can make a risk-free profit by buying pens in one market and selling in the other. So here PPP requires a 1 for 1 exchange rate.
Now suppose country A has an inflation rate of 50% and country B has 0% inflation. If inflation in country A impacts every good equally, the price of a pen in country A will be $30 on January 1st, 2021. Since there is 0 inflation in B, the price of pens will be ₹20 on January 1st, 2021. If PPP holds, we will not be able to make money from buying a pen from B at ₹20 and selling them to A at $30.
If $30 = ₹20, then ₹1 =$1.5.
Thus, the Rupee-to-Dollar exchange rate is 1.5, meaning that it costs 1.5 dollars to purchase 1 rupee on the foreign exchange market.
But for PPP to hold good:
- There should be no barriers to trade or arbitrage.
- There should be no transaction costs.
- The good has to be homogeneous.
However, these conditions generally do not meet. So, the actual exchange rates in real life differ from PPP. These differences are known as real appreciation/depreciation of a currency. Since PPP has its effect, in the long run, an economy that has a higher inflation rate than that of the other, the currency of that economy should trade at a discount in the forward market against that of another currency.
Interest Rate And Currency
Similar to how we learned the relationship between inflation and currency in the previous unit, we will now learn the relationship between interest rates and currency. So, without any further ado, let’s get started:
In the short-run, the most important factor affecting an exchange rate is the interest rate. The relation between the exchange rate and interest rate is known as Interest rate parity (IRP).
IRP states that if the interest rate in one currency (say currency B) is less than the interest rate in another currency (say currency A), currency B should be at a forward premium to currency A. More specifically, currency B should be at a forward premium against currency A approximately to the extent of the interest rate differential.
Interest rate not only helps in determining the forward premium/discount of one currency against that of another but also helps in determining the movements in spot exchange rates through a phenomenon known as carry-over trade. A carry-over trade is when we buy a high-interest currency against a low-interest currency.
For example, if INR has a 5% interest rate and USD has a 2% interest rate, we buy INR/USD. We make a carryover trade.
Money Supply
An exchange rate depends on the demand and supply of a currency, strong economic fundamentals, good ratings, and a performing equity market boosts the foreign investors’ confidence in the Indian market and attracts foreign capital in India in the form of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Institutional Investment (FII) or Foreign Portfolio Investor (FPI).
Here are a few differences between FDI & FPI:

In general, FDI is seen as a better form of investment in a country.
The huge inflow of foreign funds into the country increases the supply of USD against the Indian rupee and hence USD depreciates, on the contrary, a non performing Indian market compels foreign investors (especially FIIs) to exit the markets and hence the supply of USD against the INR falls and the USD appreciates.
When Indian equity markets are at their peak, they can attract a lot of foreign inflows, and as INR appreciates strongly, whereas the global financial crisis leads to a withdrawal of global liquidity from India, leading the INR to depreciate.
Money Supply:
The money supply is the amount of money available in an economy.
There are three main money stock measures:
M1 = Currency with Public + Demand deposits (DD) + other deposits with RBI
M2 = M1 + Time deposits with short maturity (less than 1 year).
M3 = M2 + Time deposits with a maturity of more than 1 year.

M3 is generally used to measure the money stocked in an economy all over the world.
A change in money supply can have a significant effect on the economic activity of a country, price level, and inflation. Growth in money supply with stable money demand leads to inflation. Thus, it is an important factor affecting exchange rates and the monetary policy of an economy.
The major factors that affect the money supply in an economy are:
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), Repo rate, Reverse Repo, Bank Rates, etc. Any increase (decrease) in the given rates decreases (increases) the money supply.
- FII inflows.
Impact of an Increase in the money supply by RBI:
- Leads to a fall in interest rates.
- Spot exchange rate depreciates as lower rates divert capital flows.
- Forward premium fall led by a decrease in interest rate differentials.
Impact of a Decrease in the money supply by RBI:
- Leads to a fall in interest rates.
- Spot exchange rate appreciates as lower rates divert capital flows.
- Forward premium rise led by an increase in interest rate differentials.
Market Psychology for Currency markets
Trading strategy in currency movement will depend largely on market psychology. It influences the forex market in a variety of ways:
Flights to quality
Bad international political conditions can lead to what is known as "flight to quality" in the forex market. A flight from an "uncertain" currency leads an investor to search for a "safe haven" currency. The Swiss franc is a good example of a safe haven currency because it is very stable during times of political or economic uncertainty.
Long-term trends
Although currencies do not have clear growth trends like commodities and stocks, they are often seen moving in long-term trends. Cyclical trend analysis can give us a look at longer-term price trends that may rise from economic or political trends.
Buy the rumor, sell the fact
This popular market maxim applies to many who try to anticipate a particular action and react in exactly the opposite manner. This is also referred to as the market being "overbought" or "oversold." This can be measured through technical analysis.
Market Movers
Stocks managed by hedge funds can influence the price levels to a certain degree. When the market approaches a support or a resistance level, the market behavior becomes more technical, which can result in a dramatic price swing. The movement of funds across asset classes like equity, commodities, real estate can influence currency movements.
Volatility
Generally, a high yielding currency tends to appreciate and the low yielding currency tends to depreciate. However, during times of high volatility, this statement reverses as the low yielding currency (USD, Euro, Yen, Swiss Franc, etc.) tends to serve as a safe haven for the investors. The fact that due to rising volatility in the global financial systems, equity inflows into emerging countries fall which can lead to a fall in the demand for that currency.
Since 2000, there have been 3 notable instances when the volatility of the global capital markets was very high, measured by the Volatility Index (VIX). Vix is a measure that measures short term market volatility, as conveyed by S&P 500 stock index option prices.
During the terrorist attacks of September 11, during the ongoing Sub-Prime crisis, and in 2020 the COVID-19pandemic has resulted in tremendous volatility levels. During these instances, it was seen that the USD strengthened significantly against most of the high yielding currencies like the Russian Ruble, Indonesian Rupiah, Philippines peso, Indian rupee, etc.
The primary reason behind this is that during the time of uncertainty the investors tend to favor low yielding but safer currencies/ investment destinations in comparison to higher-yielding but risky currencies/investments.

The above chart shows the Level of VIX vis a vis the levels of USDINR and the Dollar Index.
Current Account Balance
A current account is one of the components of Balance of Payments and also has a significant impact on the USDINR movement.
Current account Balance = Balance of Trade + Net Factor Income from Abroad + Net Unilateral Transfers from Abroad
A current account surplus increases a country's net foreign assets by the corresponding amount, whereas a current account deficit does exactly the opposite. Hence a current account surplus strengthens the economy and it means more of the foreign currency coming in than going out. But as we know an exchange rate involves currencies of two economies hence the relative strength of one economy's current account against another plays an important role in determining the strength of one's currency against another.
However, comparing the absolute balance of a current account of one country against that of another is not an appropriate measure of determining the growth of an economy. Hence comparing a current account as a percentage of GDP seems a more viable option.

In the above image, we can see that the Current Account BOP of India and USD/INR spot prices shows a positive relationship between them.
Current account differential also determines whether one currency would be at a premium or a discount to that of another.
Crude Oil
Crude oil is one of the most important commodities of a country's import or export bill. The US is the biggest consumer of oil and with India also moving up in that list, oil has become an important factor to analyze.
For a country like India which imports more than 70% of its crude oil requirement and crude oil being priced in USD makes it all the more important factor affecting USD/INR exchange rate. A rise in the0 price of oil can increase the demand for the dollar as oil is priced in the dollar, which can result in the dollar depreciating.
For example, an oil company imports 100 barrels of crude oil at $80/barrel. Now the price of a barrel is $100 instead of $80 and due to the rise in prices, the company now has to spend $10,000 instead of $8000 to import the same quantity of oil. This leads to an increase in demand for the dollar, which is compensated by supplying an additional rupee.

In this graph, it is quite evident that rising crude prices can lead to the depreciation of the rupee.
Major International Currencies
In this unit, we will discuss a few major currencies that are known internationally:
INR:
Indian Rupee (INR) trades against US Dollar (USD) under the managed floating exchange rate regime. This means that though the Indian rupee has a market-determined exchange rate, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) trades actively in the INR/USD currency market to impact effective exchange rates. A managed or dirty float is a currency regime for an Indian rupee for the US dollar. RBI intervenes in the currency markets only for ensuring there is low volatility in exchange rates and doesn't take a view on the direction of the Indian rupee concerning other currencies.
INR is fully convertible on India’s current account, but not on the capital account except for certain transactions carried out by foreign institutional investors who can fully repatriate their investments.
Indian companies have also been permitted to invest, up to 400% of its net worth of $1 billion, in shares of foreign companies; Mutual Funds are permitted to invest in ADRs/GDRs of the Indian companies, rated debt instruments also invest in equity of overseas companies with an overall cap of $1 billion.
Furthermore, under the Liberalized Remittance Scheme of $250,000 resident individuals are free to hold and acquire shares, immovable property, or any other asset outside India without prior approval of RBI, enabling them to convert their rupee-denominated assets into foreign currency denominated assets. These are steps closer to the full convertibility of the rupee.
All of these measures can have an impact on the exchange rate of ₹ as well as the forward premium of $/₹ and developments on these fronts are noticed by corporate hedgers, traders, etc. active in the Indian foreign exchange market.
On 29th August 2008, the National Stock Exchange of India launched the much-awaited currency futures market in India. This is a crucial event in the Indian financial market as resident Indians such as SMEs with exposure to dollar risk, students, outbound tourists, and patients planning to travel abroad for treatment can hedge their foreign currency risks through this instrument. So far there have only been bilateral currency futures contracts over-the-counter trades, but with the commencement of currency trade on the exchanges, the process becomes much more transparent.
US Dollar:
At present, the U.S.D remains the world's foremost reserve currency. The majority of U.S. notes are held outside the United States as reserves. The holdings of the US dollar bank's deposits which are held by the non-residents of its currency is known as Eurodollars. The United States can maintain its trade deficits without causing its currency to depreciate and the flow of their trade to readjust because of the overseas demand for the dollar. However, more recently, after large-scale bailouts in the current financial crisis, Paul Samuelson has said he now believes that at some stage in the future these pressures will precipitate a run against the U.S. dollar with serious global financial consequences.
The following chart illustrates the dominance of the USD in the World Economies:

Source: Wikipedia
Dollarization:
Nations other than the United States also use the dollar as their official currency, this process is known as dollarization. For example, Panama uses the dollar alongside the Panamanian balboa as their legal tender since 1904 at a 1:1 conversion rate. Ecuador, El Salvador, and East Timor adopted the USD independently. 2 British dependencies also use the U.S. dollar: 1) the British Virgin Islands and, 2) the Turks and Caicos Islands.
Other countries also link their currency to the U.S. dollar at fixed exchange rates. The local currencies of Bahamas and Bermuda can be freely exchanged at a ratio of 1:1 USD. Argentina used a fixed 1:1 exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and Argentine peso from 1991 until 2002. The currencies of Belize and Barbados are convertible at an approximate 2:1 ratio. In Lebanon, $1 is equal to 1509.69 Lebanese pounds and is used to interchange with the local currency as de facto legal tender. Since 1983, the exchange rate between the Hong Kong dollar (HKD) and USD has been linked at 7.8 HKD/USD, and Pataca of Macau is linked indirectly to the U.S. dollar at roughly MOP8/USD. Several oil-producing Arab countries on the Persian Gulf, including Saudi Arabia, peg their currencies to the dollar because the dollar is the currency that is used for international oil trades.
USD because of its strong pedigree and influence on global economics is a very important indicator to be followed for any local currency movements. The tracking of a dollar can be done through Dollar Index.
US Dollar Index:
The U.S. Dollar Index (USDX) is created by the New York Board of Trade (NYBOT). It was established in 1973 for tracking the value of the USD against other currencies, which, at that time, signified the largest trading partners of the U.S. It began with 17 currencies of 17 nations, but the launch of the euro joined 12 of these into one. So, the USDX tracks 6 currencies currently, including the euro. After ICE took over the NYBOT exchange, this index is now a part of the ICE trading platform. Following is the composition of the Dollar Index.

Euro:
The Euro (€) is the official currency of the European Union's (EU) 16 of the 27 member states. The states, known collectively as the Eurozone, are Belgium, Cyprus, Greece, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Austria, and Spain. The currency is also used in another 5 European countries, both with and without formal agreements.
The euro has more than €1.3 trillion in circulation as of Dec. 2019. The euro has the highest combined value of cash in circulation in the world, surpassing the U.S. dollar. Based on the estimates of 2019 GDP and purchasing power parity among the various currencies, the European Union is the 2nd largest economy in the world.
Since its introduction, the euro has been the 2nd most widely-held international reserve currency after the U.S. dollar. The share of the euro as a reserve currency has increased from 17.9% in 1999 to 20.67% in 2020. The euro becoming the first international reserve currency has now a real chance. Former Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan gave his opinion in September 2007 that it is "absolutely conceivable that the euro will replace the dollar as a reserve currency, or will be traded as an equally important reserve currency."
Euro is a highly volatile currency, particularly with USD. The ECB targets interest rates rather than exchange rates and, in general, it does not intervene in the foreign exchange rate markets, because of the implications of the Mundell-Fleming Model. This model suggests that a central bank cannot maintain the exchange rate and interest rate targets simultaneously because increasing the money supply results in a depreciation of its currency.
After the Single European Act, the EU has liberalized its capital markets, the ECB has been chosen as a monetary autonomy, the exchange rate regime of the euro is flexible, or floating. This explains why the exchange rate of the euro against other currencies is seen by strong fluctuations. Most notable are the fluctuations of the Euro v/s the U.S. dollar. However, this focus on the dollar-euro parity is subjective. This is a subjective reference because the euro competes with the dollar, as a reserve currency. This reference has a misleading effect because it gives observers an impression that a rise in the value of the euro against the dollar is the effect of the increased global strength of the euro, but actually, it is the effect of an intrinsic weakening of the dollar itself.
On 22nd Jan. 2015, the euro fell to $1.12. This happened because the ECB announced that they will purchase 60 billion in euro-denominated bonds each month starting in March. This method of quantitative easing gave a boost to the EU's economy, which had been struggling with a recession.
On 2nd Jan 2019, the euro was valued at $1.14. It started to fall throughout the year because the investors preferred the U.S. dollar because they were concerned about the decline of global trade due to former President Trump's trade war. By August 16, the euro fell to $1.11.
Yen:
The Yen (sign: ¥; code: JPY) is the only currency of Japan. JPY is one of the most traded currencies in the world and is widely used as a reserve currency. Yen is also considered the principal source of funds for global markets. The high savings rate and low-interest rates in Japan prompt the Japanese investors to park surplus Yen funds in international assets.
Currency Markets In India
Banks take a huge part in a country’s currency market. It is an OTC market. With the introduction of futures contracts, the market has witnessed wide-scale retail participation.
INR Futures Contract:
- Monthly contracts launched by SEBI & RBI on NSE and MCX-SX platform.
- Contracts available for 12 months. Currently, the first 3 months' contracts are the most liquid ones.
- Standardized contract specification prescribed by RBI.
- The cumulative average daily volume of over INR 5000 crores.

Advantage of Exchange and Margining System:
1.Presence of clearing corporations to protect the market.
2.Learn from mistakes:
- Current global financial as well as Indian currency market turmoil due to OTC products with no margin protection.
- The whole world is moving in favor of exchange-traded products now. The philosophy of corporate finance is changing.
3.Daily mark to market helps in real-time risk management and negates the possibility of over leveraging.
4.Although banks are not charging margins, the cost charged by them includes the cost against the risk associated with the trades.
Conclusion
Research tools for Currency market
1. Understanding various macro-economic factors and tracking various global economic data releases can help in timing the market movements.
2. Tracking INR movement through technical analysis can give a very smart indication of the probable move.
3. A view of the Indian equity market helps in understanding the FII money flow, which is one of the important factors for consideration.
4. Daily actions by the apex body RBI gives a good indication of their intentions of keeping INR at a particular range/level.
5. And most important, tracking the movement of other global currencies, will give insight into the global trend.
A currency market is a very integral part of our life. As a macroeconomic indicator, it gives a fair reflection of the economic state of the affair.
Futures are not a substitute for forward contracts. It can act as a very good complementary trade to manage the large forward deals. It helps in-
- Real-time Risk Management
- Timing Core Business Decisions
- Tracking Profit/loss
- Removing Counterparty Risk
- Price Advantage over forward in case of small tick size
- Price Transparency
So, we hope you enjoyed the learning from this module and are ready to start trading the currency markets. There are also many such modules we have designed so that you can learn the complexities of financial markets extremely well. Check out all the modules under ELM School.
Happy learning !!


