Stock Market Terminologies
Introduction
'Stock market,' became a widespread term among the millennials in the last decade. When you are just starting your investment journey, learning a few common jargons related to the stock market is essential. This module will help all novice stock market participants to learn some of the common terminologies related to the financial & capital markets. If you try reading any business newspaper like Business Standards or The Economic Times, there are many such terminologies used that you may find difficult to understand. So, let us get familiar with these terms that will help you understand and interpret the markets better.
Financial System
What is a Financial System?
First, let us get a basic idea of the financial system. In any country, economic resources are limited & scarce, with individuals having unlimited wants & desires. However, it is a challenge for the economy to determine when, where and whom to distribute its resources. Therefore, it resulted in a financial system structure capable of efficiently allocating the economic resources to stimulate growth & prosperity in the economy.
A financial system is a set of economic arrangements where several financial institutions facilitate the transfer of funds between borrowers, investors & lenders. The goal is to distribute economic resources efficiently and effectively to promote growth within the country.
Some Key features of a financial system are:
- It consists of institutions like banks, insurance companies & stock exchanges that permit the exchange of funds between borrowers and lenders.
- It offers investors the ability to grow their wealth & assets.
- It serves as a catalyst that provides opportunities such as providing savings options through banks, bringing liquidity to financial markets through stock exchanges & protecting investors from any financial risk through insurance companies.
Financial Institutions
As we have learned earlier, a financial system consists of several financial institutions such as banks, etc. Financial Institutions are intermediaries between lenders & borrowers of capital. They bridge the gap between investors (savers of capital) and companies & Governments (borrowers of capital) through several financial instruments.
The four major types of financial institutions are:
- Banks
- Investment Companies
- Insurance Companies
- Broking Firms
Let us discuss each one briefly:
Banks
Banks are a very important part of the economy because they provide vital services for both consumers and businesses. They are financial institutions licensed to receive deposits and give loans. They also provide financial services such as wealth management, exchange of currency, locker services, and many more. There are several different kinds of banks like retail banks, commercial or corporate banks, and investment banks. In India, banks are regulated by the central bank - RBI.
You can read more about them in our Banking Module.
Investment Bank
Investment banks or Merchant Banks specialize in providing services designed to facilitate business operations, such as capital expenditure, financing, and equity offerings, including initial public offerings (IPOs). They commonly offer brokerage services to investors, act as market makers for trading exchanges, and manage mergers, acquisitions, and other corporate restructurings. JP Morgan, Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, Citi Bank, Nomura, Macquarie, etc are a few globally reputed Investment Banks with operations in India.
Insurance Companies
The insurance companies offer risk management in the form of insurance contracts. The basic concept of insurance is that one party, the insurer, will guarantee payment for an uncertain future event. Meanwhile, another party, the insured or the policyholder, pays a premium to the insurer in exchange for that protection on any uncertain future occurrence.
Allianz SE, AXA, Prudential Life, Nippon Life, and MetLife are some of the biggest insurance companies globally. However, the Indian market continues to be dominated by The Life Insurance Corporation (LIC).
Broking Firms
Broking firms bring buyers and sellers together at the best possible price and extract a commission for their services. Apart from Broking, Wealth Management, and Financial advisory services are the niche services of broking firms. It acts as an intermediary between the market participants & the stock exchange. Zerodha, Upstox, Kotak Securities, Motilal Oswal, and Sharekhan are some noteworthy broking houses in the country.
Let’s discuss some common terminologies related to Account opening in a brokerage firm.
Trading A/C: It provides a platform where users can electronically buy and sell different financial assets like stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies. The stockbrokers facilitate the opening of trading accounts. One cannot trade directly on the exchange. It has to be done via SEBI registered brokers. It allows you to trade in multiple stock exchanges simultaneously.
DEMAT A/C: A Demat account is a place where shares are kept safely in electronic form. The Demat account acts as a librarian. It maintains all the records of financial securities and is stored electronically. For this service an account maintenance fee is charged known as annual maintenance charges (AMC).
POA: In general terms, POA (Power of Attorney) is a legal document that enables a person to make decisions and take actions on your behalf.
In the stock market, Power of Attorney is a document signed between the client and the brokerage firm. POA document gives limited authority to the stockbrokers to sell shares in the stock exchange from the client’s Demat account. But recently, there were several instances of stockbrokers trading through the clients' accounts without their consent. So, the market regulator SEBI issued new guidelines for POA; now, a broker's authority is only limited to the transfer of securities & funds from clients' Demat and bank accounts.
BSDA: A basic service Demat Account (BSDA) is a type of Demat account, which is intended for small investors.
The charges to maintain this account are lower than normal Demat A/C.
This was introduced in 2012, as SEBI felt the majority of the investors were using the account very little but still were paying high maintenance charges.
An investor cannot have both regular and BSDA accounts open at the same time.
The limit for investment value in this account is ₹2 lakhs for BSDA in case it exceeds the amount, the brokers can charge as high as normal Demat A/c.

E-KYC
KYC stands for ‘Know your customer.’
To open a trading account with a SEBI-registered intermediary, one has to submit personal details, which will then be verified by the intermediary. It is done to prevent frauds such as money laundering and customer fake accounts.
The KYC process necessitates the following documents:

After the details have been verified by the intermediary, an account with a broking firm can be opened.
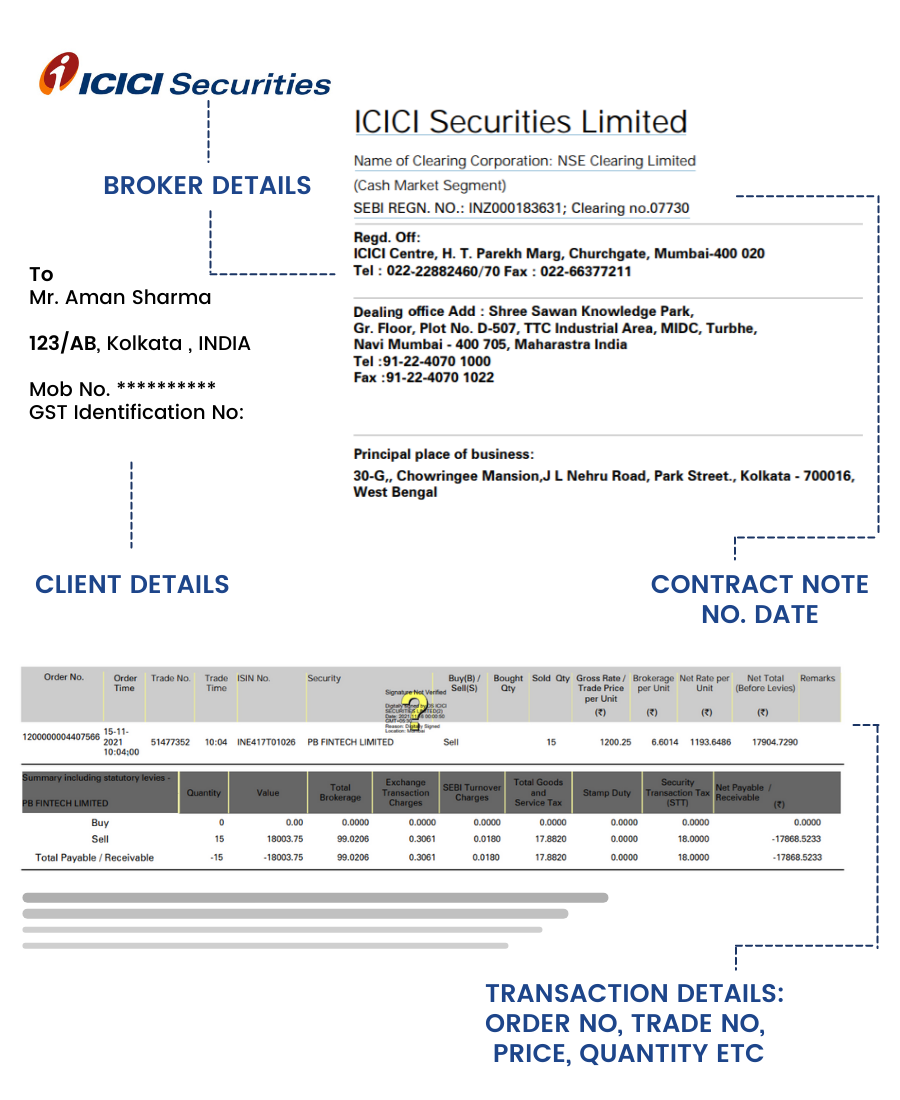
Contract Note: Contract notes are one of the most relevant legal documents available to market participants in the stock market. This is because it records all the necessary details with respect to the transaction undertaken and also all details about the profit and loss incurred. It records all the transactions or trades on a particular day, brokerage fee and taxes. It is basically a reference point for clients to see their trades and get all the information at one place like date, period, size; quantity exchanged, etc. It also mentions a reference number that can be used to cross-check transaction information with the stock exchanges. The contract note is in a standardized format which is prescribed by the stock exchange.
The following details are mandatory to be in a contract note.
- Name, address, and SEBI Registration number of the stock broker.
- Authorized Signatory for the stock broker.
- PAN of the stock broker.
- PAN of the Investor.
- The Contract note number, date of issue , the settlement number, and the period for settlement.
- The order number and time
- The trade number and time.
- The quantity and details of securities bought/sold
- The trade price and the brokerage
- Service tax rates and any other charges.
- Securities Transaction Tax as applicable.
- Authorized Signatory’s signature of the stock broker.
Note: DP Charges, margin details, and outstanding positions of the client don’t reflect in a contract note.
Margins: Margin Trading is a form of loan by the broker to the client to buy securities in excess of his account balance. For example, XYZ Broking Firm offers its clients a 3X margin on delivery trades. This means that an investor can purchase stocks worth ₹300 with an actual account balance of ₹100. Needless to say, the broker charges a nominal interest rate for this facility.
Pledging: Simply put, pledging of securities refers to mortgaging financial securities such as stocks, bonds, debentures, etc. Traders pledge their stock & ETF holdings to receive margin funding from the broker. The investors are entitled to all corporate benefits such as dividends, right issues, etc on their shares while they remain pledged.
Types of Financial Instruments
Let us now discuss some common financial instruments:
Equity shares: An equity share or commonly known as stock represents the ownership of a fraction of a company. Stocks are bought and sold on the exchanges among investors or traders. Example: Reliance Industries (RELIANCE) is a stock traded on the exchange.
Bonds: A bond is a fixed-income instrument. Bonds are agreements to lend money to a company for a certain period against which the company needs to pay a fixed interest. A company sells these securities to get the money it needs to grow.
Mutual Funds: Mutual funds are another financial security that is one of the most popular investment options currently. When an Asset Management Company (AMC) pools investments from different individuals that have a common investment objective. Mutual funds are professionally managed, so it is elementary for novice investors to start their financial journey. In recent years the mutual fund industry has grown almost two-fold within a span of five years.
G-Secs: Government Securities or G-Secs are debt instruments issued by the government to borrow money. In case of a bond you lend money to a company, similarly in case of G-Secs you lend to the Government and in return they pay a fixed rate of interest for a predetermined period of time.
SGBs: Sovereign Gold Bonds or SGBs are government instruments denominated in terms of Gold. These are substitutes for holding physical golds. Investors buy SGBs in return for capital appreciation as well as earn fixed interest every six months.
ETFs: An Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) are a basket of financial instruments which may include stocks, commodities, bonds or a mixture of different instruments. Thus, ETFs offer diversification to investors. There are also ETFs that track an index, sector, commodity, or other asset. Example: HDFC Sensex ETF
REITs: REITs (Real Estate Investment Trust) is a financial instrument that owns a portfolio of income-generating properties. This is very similar to a mutual fund where money is pooled from investors to invest in financial securities; in the case of REITs, pooled money is invested in real estate.
In India, REITs were introduced in 2019. After 2 years, three REITs are available for Indian investors (Mindspace, Embassy Park & Brookfield). Similar to an investment in common stocks, profits are generated in the form of dividends & capital appreciation. SEBI is the regulator of REITs in India.
InVITs: Power Grid InVIT & India Grid InVIT are two names that are all over the news recently. So let us see what InVITs are?
Infrastructure Investment Trust (InVITs) is a financial instrument that offers a direct investment route into infrastructure projects for both individual & institutional investors. The structure of InvITs is closely related to mutual funds & REITs. Therefore, InVITs are a collective investment scheme that offers a direct investment into infrastructure. SEBI is the regulator of InVITs India.
IPO
Before we learn the different terminologies related to IPO, financial markets are broadly divided into two segments: Primary Market and Secondary Market. Let us first understand what is primary market and secondary market and the basic concept of IPO.
Primary market: The primary Market helps companies, governments, and other financial institutions raise funds in the market for the first time. This is done through the sale of various debt and equity-based securities. For example, when a company decides to raise funds from the public, they sell part ownership of their company through the issuance of equity shares.
Secondary market: This is where the securities listed on the exchanges are traded amongst investors. These are the same shares initially offered by the company in the primary market and now can be freely traded by the investors. The important thing to note here is that all secondary market transactions are between investors or traders. The company is not directly involved in it. The secondary market provides the option of exiting the shares bought in the primary market or making new entries in stock. The primary function of the secondary market is to offer investors liquidity for their assets, and they can buy and sell at any time during the market hours.
What is an IPO?
When a company decides to go public, it decides to float an Initial Public Offering or IPO through the primary market route. A company raises capital for various reasons, such as business expansion, meeting their working capital requirements, paying off debts, investing in new projects, etc.
For Example, Company A Limited requires funds to invest in a new project and is looking to expand their business. It issues shares in the primary market. When the company issues shares for the first time, it is called Initial Public Offering (IPO).
A further issue of shares is known as Follow-on Public Offer (FPO). When a company is already listed in the public exchanges and needs more capital from the public, they launch FPO.
Both IPO & FPO issuances fall under the ambit of Primary Markets. Let us now discuss some common terminologies related to IPOs:
ASBA: ASBA (Applications Supported by Blocked Amount) is a kind of application that is authorized to block the application money in your bank account for subscribing to any public issue. If you are applying through ASBA, the application money shall be debited from your bank account only if the application is selected for share allotment, otherwise not if the issue is withdrawn or failed.
Authorized Share Capital: The maximum amount of the capital against which the number of shares can be issued by the company to their shareholders. The Authorized capital is detailed in the Memorandum of Association (MOA) of the Company.
However, at any time in the future, the Authorized capital can be increased as per necessary requirements by the company.
Paid up capital: The amount of capital for which the total number of shares of the company were issued and payment was duly made by all the shareholders. It is possible that at any point in time, paid-up capital will be less than or equal to authorized share capital. But the company cannot issue shares beyond the authorized share capital of the company. With the introduction of the Companies Amendment Act 2015, there is no minimum requirement of paid-up capital for the company. It means now any company can be formed with even ₹1,000 as paid-up capital.
Subscribed share capital: When members subscribe to the shares of a company, Subscribed capital increases. Subscribed share capital must also be equal to or less than the issued share capital. The un-allotted capital out of the subscribed share capital is called unsubscribed share capital.
Red Herring Prospectus (RHP): This is a document that contains all information about the company going public, such as business operations, financials, promoter's details and the reason for raising money through IPO. So, studying the RHP helps to decide whether to subscribe to the IPO or not.
Grey Market Premium (GMP): A grey market is an unlisted marketplace where participants buy and sell IPO applications among themselves in exchange for money. Therefore higher the premium, the higher is the possibility of staggering listing gains.
Stock Exchange
Previously we have learned after an IPO, the stocks are traded over the exchanges among investors and traders. In this section, we will discuss some common terminologies related to the stock exchanges. But before we start, let us first understand the concept of stock exchanges.
What is a Stock Exchange?
The stock exchange is a trading platform where buyers & sellers meet to complete the purchase/sale of financial securities such as stocks, bonds, currencies, etc. Stock exchanges act as a forum for price discovery. The National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) are the two major electronic exchanges in India.
Let’s learn some terminologies that are related to stock exchanges:
Index: An index can be thought of as a collective report card. In an army of more than 5,000 listed stocks on the exchange, it becomes impossible to track each and every stock to decide if the market is up or down for the day. An index simplifies this by bringing together a selected group of stocks to gauge the performance of the market. Indexes can be classified in terms of market capitalization, sectors, momentum, or any other suitable criteria.
The S&P BSE Sensex or Sensitive Index is a market-capitalization-weighted index representing a basket of thirty most active, liquid & representative stocks on the Indian bourses. It was first compiled in 1986 with a base value of 100.
The other widely tracked bellwether, The S&P CNX Nifty 50 Index is also a market capitalization-weighted index of the fifty largest & the most-liquid blue-chip Indian securities listed on the NSE. It was first compiled in 1996 with a base value of 1,000.
Bull & Bear market: In a bull market, mostly all stock prices continue to rise over time; on the other hand, in a bear market, prices continue to decline over time.
The market rise or fall can be attributed to several factors such as a positive economic outlook, strong corporate earnings, etc., and vice versa in the case of a declining market.
Dematerialization: When the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) was established in 1875, stocks were in physical form called ‘Share certificates’. These were regarded as proof of ownership.
Nonetheless, this process led to a great amount of paperwork, and the settlement of trades took weeks. The risk of theft, damage, or loss of certificates came with this process. The trading process was completely digitized in 1996 & along with it came mandatory dematerialization of securities.
Dematerialization is the process by which security held by an investor in physical form is converted into electronic securities and credited into an investor’s Demat account.
This was earmarked as a revolutionary step since real-time trading greatly reduced transaction costs & brought about complete transparency in the trading process.
Market Capitalization
Market capitalization is the market value of the company. It is calculated by multiplying a company's outstanding shares with the current share price of a stock (CMP). Outstanding shares are the total shares of the firm. It includes those shares also which are not freely traded on the stock exchange.
For example – HDFC Bank Ltd. Has approximately 554 Crores shares issued. The current market price of the stock as of date 26Th October 2021 is ₹1653. Hence the approx. Market cap of the stock is 1653 * 554 Crores which equals 915692 Crores.
Based on their size, companies are further classified into:
Large Cap - Companies with a market capitalization of more than 4000 crores, are included in this group. These are well-established companies in the market with a stable business structure, like Kotak Mahindra Bank, TCS, Reliance Industries, and many more big companies you probably may hear the name of.
Medium Cap or Midcap – Companies are mid-sized companies with a market cap of more than 250 crores and less than 4000 cr. These companies are at the stage of growth and development. Investors usually prefer to buy mid-cap stocks for their potential growth.
Small Cap - These companies have a market cap of less than 250 crores. These companies have an emerging business. Investors who prefer high risk and high return invest in small-cap stocks.
Trading
Here is a list of common terminologies used while trading in the stock market:
Stock symbol: The stock exchanges create a stock symbol for accessible communication among market participants. It is simply a short form of the company name. For example, Kotak Mahindra Bank, the symbol is 'KOTAK BANK.'
Tick Size: Tick size is the smallest possible increment or change in the price of a security. It can also be thought of as the minimum spread between bid-ask rates. The tick size for all stocks listed NSE & BSE is fixed at ₹0.05. It means that the stock price will change in multiples of ₹0.05. To put in another way, stock can be bought/sold either at ₹100 or ₹100.05 but not at ₹100.02
Note – Mutual Fund Units, ETFs, Fixed Income Securities and Stocks priced less than ₹15 on the BSE have a tick size of ₹0.01.
Bid & Ask Spread: Bid price is the price at which buyers are willing to buy a particular stock
Ask price is the price at which sellers are ready to sell the stock.
Bid-ask spread is the difference between the best bid rate and the best ask rate.
Extreme bid-ask spreads signify lack of liquidity. Higher the liquidity in the market, lower the spread, better the price discovery and vice-versa.
LTP Price: This is the most meaningful information in a stock quote, i.e., the current market price, or you can call it last traded price (LTP), which means the price at which the latest trade is executed on an exchange between a buyer and a seller.
LTQ: The last traded quantity at a particular point in time during the market hours. Therefore, it constantly changes as it shows the latest information on traded quantity.
Open-High-Low-Close: The price at which the day's first trade gets executed and stocks start trading for the day in the exchange is the open price. High and the Low prices are the highest and the lowest price traded on the particular trading session. Finally, the closing price is the price at which the last trade got executed at the end.
Volume: The volume of a stock is the total number of shares traded on financial security during a given time period.
Volume figures are also displayed at the bottom of price charts.
The volume of a stock is perhaps the single most important factor tracked by technical analysts. If a stock rises with high volume, it indicates a lot of strength and it is likely that the momentum will continue on the upside & vice-versa. When we talk about higher or lower volume, it is relative to average volume over certain time periods.
Volumes are generally low when the stock is in a consolidation/ range-bound phase.
Delivery: Delivery Percentage is another important concept to take note of while we study volume.
Trades entered & squared off in the same trading session are intraday trades. However, if the investor decides to keep the position for more than one trading session i.e., carry forward the position & take delivery of the shares, the exposure becomes positional.
It is also important to check the delivery percentage of a stock along with its volume. Higher the delivery percentage of stock, the greater the strength of the underlying momentum.
52 Week High/Low: The 52-week high/low is the highest and lowest price level at which a stock quoted in the past one year. 52-week high lows act as a strong resistance/support level.
Market Depth: Market depth is the measure of demand & supply of an asset traded on the exchange. It is real-time data of open buy and sells orders for given security on the exchange. This is an electronic list split into those willing to buy and others ready to sell.
Say, if we want to buy a stock, there has to be a seller willing to sell the stock at a fair price, i.e., 'Ask price,' and the price a buyer is willing to pay is 'Bid price.' Market depth offers buyer/seller order quantity and price, time of placing the order, best 5 bid/ask prices. It is a helpful tool for traders or investors to get an idea of market participants in that stock who are willing to buy and eager to sell the stock and what prices they are quoting for any particular quantity. A market depth depicts liquidity on the specific security.
Circuit Breakers: The mechanism behind circuit breakers is intended to protect traders and investors from sudden surge/plunge in the price of the security.
Circuit breakers are predefined values in percentage terms, which trigger an automatic check when there is a runaway movement in the price of a security/index in either direction. The values are calculated from the previous closing level of the security or the index. The exchange, to avoid manipulation and erratic price movements, only allows stocks to change hands at a price equal to or less to the circuit limit.
For stocks trading in the Cash Market, the circuit limit ranges between 2% to 20% for different stocks.
For instance, the stock of ABC Corporation Ltd has a 10% circuit filter and closed at ₹100 the previous day. For the next trading session, the stock can only move in a range between ₹109.95 on the higher side & ₹99.05 on the lower end.
For stocks trading in the Cash Market, the circuit limit ranges between 2% to 20% for different stocks.
There are generally two types of circuit breakers:
- Upper circuit: The limit at which stocks cannot rise above for that day. Say stock of ITC is trading at 200 and the upper circuit of the stocks is at 240 (20%). Suppose on a particular day the price went to 240. ITC stock price cannot go higher than 240, however trading can take place at the same price or lower.
- Lower circuit: This is the limit below which the stock trading gets halted for the day. Similarly, let's say the stock of ITC has a lower circuit of 160. If the price falls from 200 to 160 in a single day, it can not trade lower than this value.
However, Stocks trading in the Futures & Options Segment do not have any circuit breakers. At the Index level, circuit filters are triggered at 10%,15% and 20% respectively .
Price Bands: There are price bands set for all securities by the exchange. The price bands serve as boundaries for the stock's trading; the exchange will not accept orders that are set outside the minimum and the maximum of the price range.
The purpose behind price bands and circuit breakers is to control mass buying or selling of shares and to avoid price rigging.
Insider trading: It refers to the buying & selling of financial securities by someone who is in possession of materially unpublished price-sensitive information about the company. Insider Trading can be legal or illegal depending upon the timing of the trade.
Bulk Deal: A bulk deal is a deal where the total quantity of shares bought or sold is more than 0.5% of the number of equity shares of the listed company. Bulk deals take place during the regular trading window provided by the broker. Thus, it is a market-driven deal. Everyone trading on the stock exchange can view the deal. The broker who executes the bulk deal is required to provide the details of the transaction to the stock exchanges. If a deal is via a single transaction, then the broker informs the exchange immediately, and if it’s done via multiple transactions, the broker informs the exchange within an hour from the close of the trading day. If 0.5% or more is bought and sold of the same stock during the same trading session, it would be deemed two separate bulk deals and require two separate disclosures.
Block Deal: A block deal is a deal in which trading is done for more than 5 lakhs shares or more than 5 crores value of a company. It takes place through a separate trading window from 9.15 am to 9.50 am for a duration of 35 minutes. The shares traded in this window should range within +1% to -1% of the current market price or the previous day’s closing price. A block deal will take place only when the two parties agree to buy or sell shares at an agreed-upon price.
Since block deals happen in a separate window, they are not visible to the regular market players. The broker needs to Inform the exchange regarding these deals too.
VIX: Volatility Index is a measure of the amount by which an underlying Index is expected to fluctuate, in the near term, (calculated as annualized volatility, denoted in percentage (e.g., 20%) based on the order book of the underlying index options. India VIX, based on the Nifty 50 Index Option prices. From the best bid-ask prices of Nifty 50 Options contracts, a volatility figure (%) is calculated which indicates the expected market volatility over the next 30 calendar days. The India VIX should be thought of as a fear gauge.
Pay In: The process of delivering shares sold by the client via the broker to the designated account of the clearing corporation is known as Pay in. The pay in of the securities should be done by 10.30 am on the pay in day.
Pay Out: The process by which the clearing corporations allocate and transfer the securities to be received by the clients who have purchased the securities via the broker.
Rolling Settlement: Rolling Settlement is a mechanism of settling trades done on a stock exchange. In the early days, NSE followed a weekly settlement cycle where the trades executed throughout the week were settled every Tuesday. However, as the financial markets evolved, the settlement time was then reduced, and it came down to T+3 days.
Today on NSE and BSE, the settlement of cash market trades is done on T+2 days. Here T is referred to as the day on which the transaction has taken place. + 2 refers to the working days. At the time of calculation of the settlement day - All holidays, like bank holidays, NSE holidays, Saturdays, and Sundays, are excluded. So ideally, trades taking place on Monday are settled on Wednesday, Tuesday's trades settled on Thursday, and so on. However, recently NSE has rolled out T+1 settlement for a few stocks and going forward this will be a common standard for stocks traded on the NSE. Example: TRIDENT INDIA.
Short-Selling: We can sell shares in stock exchanges if we anticipate that the stock price may fall going forward. So, the investor borrows a share from its broker & sells it.
Once the share price falls, we will buy the same share at a lower price and return it to the broker while pocketing a profit in the trade. The process is first to sell high and then buy low.
This helps traders make a profit from a declining stock or index. Usually, Short-selling is considered risky.
Suppose you expect shares of TCS to fall for whatever reason, then you place an order to sell shares of TCS at the current market price. After the share price falls adequately by tomorrow, you buy at a significantly lower rate.
The difference between the selling and buying prices is your profit.
However, if the share prices increase after you sell at a reduced price, then you end up with a loss.
Auction: In the stock market, trade is said to be complete between buyer and seller when the seller delivers the shares at the time of settlement (Its T+2). If the seller fails to deliver shares to the buyer, the transaction gets null & void and settled in cash. The process is called Auction.
In the Auction process- the exchange or broker decides a price on which the trade will be settled. A penalty is also imposed on top of the price for the seller & the same is passed on to the buyer.
GSM: Graded Surveillance Measure is a system that monitors stock with unusual price fluctuations or may be of poor financials. GSM comes into existence to improve market integrity and protect the interest of investors. The purpose of GSM is to alert and advise all investors to be more cautious while dealing in securities that are on the GSM list, as well as to conduct necessary due diligence before dealing in these securities. Accordingly, the market regulator SEBI & the stock exchanges have implemented this surveillance measure.
If you trade on any one of the exchanges, BSE or NSE, you may have noticed the text “GSM: Stage – 01” appears below the name of certain companies. There are a few criteria to be fulfilled before the stock is added to GSM: Stage -01 list. They are:
- Securities with a current net worth of less than or equal to 10 Crores.
- Securities with current net fixed assets of less than or equal to 25 crores.
- Securities with PE (Price to equity) greater than 2x the PE of the benchmark (Nifty 500) or Securities with negative PE.
ASM: Additional Surveillance Measure (ASM) is nearly identical to that of GSM, that is, to improve market integrity and protect investors’ interests by implementing various enhanced pre-emptive surveillance measures, but ASM is majorly focused on controlling security volatility.
Similar to GSM, ASM also has a few criteria to be fulfilled before adding the stock to the ASM list.
- High-Low Price variation
- Client concentration
- Close to close price variation
- Market capitalization
- Volume variation
- Delivery Percentage
- No. of unique PANs
- PE
Delisting: As the term suggests, the removal of publicly listed stock from the stock exchanges is known as delisting. There can be both voluntary & compulsory delisting; in case of voluntary delisting, the company internally decides to delist its shares from the exchanges. In compulsory delisting, securities are delisted from the exchanges as a penal measure for not complying with various listing agreements.
Mahurat Trading: In the Hindu calendar, Diwali is considered the 1st day of the new year. Hence, every year, the stock market is open for a few hours on the occasion of Diwali.
A trading session is conducted for an hour in the evening on the special occasion of Diwali.
This is called Mahurat trading that has been going on for over 100 years now on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
It marks the starting of a new financial year called 'Samvat.'
Finally here is a list of the stock market abbreviations that you should know while trading in the stock market.
- EQ : It stands for Equity
- BE : It stands for Book Entry. Shares falling in the Trade-to-Trade or T-segment are traded in this series and no intraday is allowed. This means trades can only be settled by accepting or giving the delivery of shares.
- BL: This series is for facilitating block deals. Block deal is a trade, with a minimum quantity of 5 lakhs shares or minimum value of Rs. 5 crores, executed through a single transaction, on the special “Block Deal window”. The window is open for only 35 minutes in the morning from 9:15 to 9:50AM.
- BT : This series provides an exit route to small investors having shares in the physical form with a cap of maximum 500 shares.
- BZ : Stocks that are blacklisted for violation of exchange rules. This series of stocks falls under Trade-to-Trade category and hence BTST (Buy Today Sell Tomorrow) and intraday is not allowed in such stocks.
- GC : This series allows Government Securities and Treasury Bills to be traded under this category.
- IQ : To facilitate QFI (Qualified Foreign Investors) to trade in companies without prior approval of the depositors where maximum permissible limit for FII’s is not breached.
- IL: This series allows only FIIs to trade among themselves. Permissible only in those securities where the maximum permissible limit for FIIs is not breached.
These abbreviations are helpful while trading on the NSE terminal.
Types of Orders
Some basic types of orders placed by market participants are:
Market orders: The simplest type of placing an order. A trading order for buying and selling a security at the best price at the current price level. It means once the buy and sell orders are entered, the trade gets executed immediately. A buy order is executed at the Ask price whereas a Sell order is executed at the Bid price in a market order.
Limit orders: A limit order allows us to set a particular price we want to buy or sell a security. Unlike market order, a limit order offers control over buying and selling a stock at the desired price.
Stop-loss order: This is very helpful for every trader and investor because it limits the losses by exiting the trade if a particular price level is reached. If any trade goes against the anticipated view, stop loss order helps in exiting the position.
For example, a trader places a buy order:
Buy Price- ₹1075.5
Stop loss - ₹1065.5
If price falls below ₹1065, the stop-loss sell order will be executed. When the trigger price is breached, the stop loss order goes into the system order book as a normal limit order and is executed. As a result, the trader will book a loss of ₹25 per share and exit the trade.
After Market Orders (AMO): It is suitable for investors/ traders preoccupied during the day & does not have time to actively track the security price. A regular market hour in India is 9.15 AM to 3.30 PM. If an order is placed beyond these timings is classified as an After-market order. Different brokers specify a particular time interval within which one can place an after-market order.
Bracket Order (BO): These are special types of trading orders placed during intraday trading only. They combine a buy or sell order with a stop-loss and target order. These orders help stock market traders to square off their profitable position by the end of the trading session or exit from a loss-making position. However, this result is entirely dependent on the selection of stock, how the trader picks the stop-loss and target levels.
A bracket order consists of three separate orders bundled into one.
- A limit buy/ sell order
- A limit sell/buy order (to book profits )
- A stop-loss order.
Eg: If the share of ABC is trading at ₹1000. We can put a bracket order to buy it at ₹1000 with a target of 10 points and a stop loss of 5 points.For every bracket order that gets executed, we have 2 corresponding orders that get placed automatically. One is the target order and another is the stop-loss order.
Cover Order (CO): In a Cover Order, an investor can take an intraday position while he/she is protected by a stop loss order, allowing them to take advantage of additional exposure. Cover order is one of the types of orders by which one can enter a position along with a stop-loss in the same order form.
Also, based on time duration there are different types of orders:
- Good For Day Order (GFD) – order will stay valid till the end of the current trading session.
- Good Till Day Order (GTD) – We can keep our order active for a few days. Eg- If we place an order on 1st March and it does not get executed, we can carry forward to say till 4th march. If it doesn’t get executed even on 4th march, the order will be cancelled.
- Immediate or Cancel Order (IOC) – These orders once placed will be executed immediately if it is not executed it will cancel itself. In this case, it may so happen that the order will be partially executed. Eg- If we place an order to buy 1000 shares and only 600 shares get immediately purchased, the rest of 400 shares will get cancelled.
Market Participants
There are different types of market participants in the stock markets. We can clearly distinguish between them based on their nature and purpose of actions:
Based on Purpose:
1. Speculators – To speculate means to bet on the direction of a particular stock/security. Speculators generate profits by anticipating future price movements.
2. Hedger - A hedger is a market participant who intends to offset his exposure and protect himself from adverse price movements. For instance, an Airline Company might go long in futures contracts on Crude Oil to protect itself from a rise in input costs.
3. Arbitrageur - An arbitrageur is a person who tries to make a riskless profit by simultaneously buying and selling the same financial security on different exchanges/markets. These days arbitrage opportunities rarely exist because of high transaction costs & algorithmic trading.
Based on Nature:
1. Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs)- FIIs are big foreign institutional investors like foreign banks, corporates, insurance companies, mutual fund houses, and even governments of foreign countries that are bringing foreign capital to India for investment. They also invest large sums of money and usually stay invested for an extended period. These players provide a lot of liquidity in the markets.
2. Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs)- DIIs are big institutional investors like Indian banks, corporates, insurance companies, mutual fund houses, and even the government of India, who are investing in the stock market. They pour large sums of money into the stock market.
3. Retail Investors- Investors like you and me participate in the stock market for trading, investment, gathering for retirement funds, and wealth creation. Retail investors have a minimal capacity for buying and selling shares. They usually invest in markets with low funds compared to others. They are primarily salaried individuals or small self-employed businessmen.
4. High Net Worth Individuals (HNIs)- HNIs are the big, influential players in the stock market who have capital of ₹2 crores or more invested in the stock market. They usually invest with significantly large funds. Common names we hear in India are Rakesh Jhunjunwala, Vijay Kedia, Dolly Khanna, etc. They all come under the category of non-institutional investors or HNIs.
Types of Market Sessions & Timings
Stock market in India operates from Monday to Friday. However, there are certain market sessions and timings. They are:
Pre-Open Market:
The duration of the pre-open market session is from 9:00 AM to 9:15 AM, i.e., 15 minutes before the trading session starts and is conducted on both NSE and BSE. The purpose of the Pre-Open Market is to stabilize heavy volatility due to some major event or announcement that comes overnight before the market actually opens for trading. Normally, retail investors are advised not to participate in this session as stock prices are excessively volatile in this period & may not be indicative of actual opening.
The pre-open market session is split into three phases:
Order Entry Session: From 9:00 AM to 9:08 AM (8 Minutes)
During these first 8 minutes, all the orders are placed to buy and sell stocks. Orders can be modified & cancelled during this time slot.
After this no further orders are accepted.
Order Matching Session: From 9:08 AM to 9:12 AM (4 Minutes)
The next four minutes are allotted for order confirmation & order matching. The opening price of the stock is calculated based on the bid-ask rates received during the order entry session. Orders cannot be modified or cancelled during this period.
Buffer Session: From 9:12 AM to 9:15 AM (3 Minutes)
After completion of order matching, there is a three-minute silent period to facilitate the transition from pre-open session to the normal market. All outstanding orders are moved to the normal market retaining the original time stamp. These three minutes are referred to as the buffer session of the preopen market session.
Normal Market
Normal Market aka continuous trading session lasts from 09:15 hours to 15:30 hours, Monday to Friday-five days a week. There are no restrictions regarding order modification or cancellation during this period & one can trade freely. All orders are matched through the order book that quotes the five best bid-ask rates for every security.
Post-closing session
This session begins after the normal market ends at 15:30 hours. The official post-closing session timings are from 15:40 hours to 16:00 hours.
From 15:30 hours to 15:40 hours, the closing prices of stocks are calculated by taking the volume weighted average of the stock prices traded during the last thirty minutes of the trading session i.e., between 03:00 PM and 03:30 PM.
At 15:40 hours, the post-closing session starts and one can still place buy and sell orders. However, the order confirmation chances are slim since there might not be enough liquidity. Trading takes place at one single price i.e. the closing price of the security. Hence, no stop-loss or limit orders can be placed during this session.
Market Timings
Trading in Indian Equity Markets takes place on five days a week- Monday to Friday. Each trading session is split into:
A) Pre-open session: The duration of the pre-open market session is from 09:00 hours to 09:15 hours.
B) Regular trading session: The regular trading session is from 09:15 hours to 15:30 hours
C) Block Deal Session Timings: There are two specific timings for block deals:
1. Morning Block Deal Window: This window shall operate between 08:45 hours-09:00 hours
2. Afternoon Block Deal Window: This window shall operate between 14:05 hours-14:20 hours
D) The Closing Session: is held between 15.40 hours to 16.00 hours.
Derivatives Market
What are Derivatives?
A derivative is a financial contract between two parties that derives its value from an underlying asset. This means that they possess no value of their own but are dependent on the asset to which they are linked. The most common types of derivatives are Futures, Options, Forwards & Swaps. Derivatives contracts can be on various asset classes like stocks, bonds, currency, commodities, and interest rates. Derivatives are used by market participants for hedging as well as speculative purposes.
Let’s have a look at some common terminologies related to derivatives:
Forward: It is an agreement for buying or selling an underlying asset at a particular price & a specific date in the future.
A buyer takes a long position on the asset, whereas the seller takes a short position or maybe vice versa. The parties involved in this contract can manage the volatility by locking in the price for the underlying assets. Forward contracts are traded over the counter & are not regulated by the exchanges so, it is possible to customize the agreement between two parties as per requirement. They are mainly used for hedging against market uncertainty. These contracts are prone to default as they are not regulated.
Futures: Futures contracts are similar to forwards contracts. But unlike a forward contract, a futures contract cannot be customized because the exchanges regulate them. Hence futures contracts are standardized agreements between two parties. Futures contracts are less prone to default because they are regulated.
Options: An option is just a contract giving you the right to buy or sell an underlying security at a pre-negotiated price on a specific date. However, when that date arrives, you’re not obligated to buy or sell the underlying. Instead, you have the option to let the contract expire. However, when buying options, you’ll pay what’s known as a “premium” up front, which you’ll lose if you let the contract expire. But when you are selling an option, you receive a premium. Hence on expiry, you get to keep the premium you receive.
There are mainly two options:
- Call option: A call option gives the right to buy an asset at a particular price at a later date.
- Put option: A put option gives the right to sell an asset at a particular price at a later date.
Swaps: A swap is a derivative contract between two parties that involves exchanging of cash flows, such that one party will receive a fixed interest rate & pay the other party a variable interest rate. The cash flows are derived from an underlying asset; hence swaps are a derivative instrument. Generally, swaps are traded over the counter market so they can be customized as per the needs of the parties in the contract.
Strike: A strike price refers to the predetermined price at which a derivative contract can be bought or sold at a future date. When entering a derivative contract, the strike price is decided at which buyer & seller will execute the contract.
Expiry: This is the date at which a derivative contract comes to an end. The expiry date is essential for both parties of the contract because, before expiration, they have to decide whether to execute the contract or not.
Open Interest (OI): Open interest is the total number of derivatives contracts outstanding in the market on a particular day. Therefore, OI data is beneficial for traders as it measures money flow in the derivative market.
PCR: PCR, also known as Put Call Ratio, is a derivative tool used by many market participants to measure the market's sensitivity. PCR is calculated by the total number of Puts divided by the total number of calls. If PCR>1, we can consider that more market participants are willing to take short positions & the market may fall. On the other hand, if PCR <1, it signifies more market participants are expecting an up move in the market as Calls are more than the puts.
Option Chain: An option chain is known as an Option Matrix is considered another helpful tool for traders. The options chain lists out all option contracts, both puts, and calls for a specific security. It shows a few key information like expiry date, strike prices, and volume and pricing information, etc.
Conclusion
Finally, we came to the end of our journey of learning several common terminologies that are used in the financial systems across different industries. We have focused especially on those terms that are commonly used in the stock market.


